
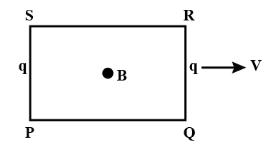
Figure shows a rectangular loop moving in a uniform magnetic field. Show the electrical equivalent of each branch.

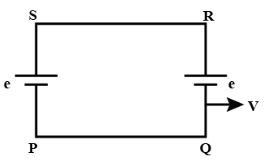
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint:The magnetic effect on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials is described by a magnetic field, which is a vector field. In a magnetic field, a moving charge experiences a force that is perpendicular to both its own velocity and the magnetic field.
Complete answer:
An equivalent circuit is a theoretical circuit that preserves all of the electrical properties of a particular circuit in electrical engineering and research. Two circuits are identical if a particular voltage is applied to the terminals, the current through the terminals is the same, and vice versa; that is, if a particular current is allowed to flow through the terminals, the voltage across the terminals is the same in both circuits.
We can replace two or more comparable passive elements in a circuit with a single comparable passive element if they are coupled in purely series or parallel mode. As a result, the circuit is referred to as an equivalent circuit. Hence from the given question,the induced emf in Branch PS and QR is identical, but no emf is induced in any other branch. Now, induced emf (e) is,
$e= VBI$
where $V$ = Potential difference, $B$ = Magnetic field, $I$ = Current and $e$= induced emf.
Note:In order to help analysis, an equivalent circuit is frequently sought that simplifies computation and, more broadly, that is the simplest version of a more complex circuit. An equivalent circuit is made up of linear, passive parts in their most basic form. More sophisticated equivalent circuits, on the other hand, are utilised to approximate the nonlinear behaviour of the original circuit. Macromodels of the original circuit are typically used to describe these increasingly complicated circuits. The Boyle circuit for the 741 operational amplifier is an example of a macromodel.
Complete answer:
An equivalent circuit is a theoretical circuit that preserves all of the electrical properties of a particular circuit in electrical engineering and research. Two circuits are identical if a particular voltage is applied to the terminals, the current through the terminals is the same, and vice versa; that is, if a particular current is allowed to flow through the terminals, the voltage across the terminals is the same in both circuits.
We can replace two or more comparable passive elements in a circuit with a single comparable passive element if they are coupled in purely series or parallel mode. As a result, the circuit is referred to as an equivalent circuit. Hence from the given question,the induced emf in Branch PS and QR is identical, but no emf is induced in any other branch. Now, induced emf (e) is,

$e= VBI$
where $V$ = Potential difference, $B$ = Magnetic field, $I$ = Current and $e$= induced emf.
Note:In order to help analysis, an equivalent circuit is frequently sought that simplifies computation and, more broadly, that is the simplest version of a more complex circuit. An equivalent circuit is made up of linear, passive parts in their most basic form. More sophisticated equivalent circuits, on the other hand, are utilised to approximate the nonlinear behaviour of the original circuit. Macromodels of the original circuit are typically used to describe these increasingly complicated circuits. The Boyle circuit for the 741 operational amplifier is an example of a macromodel.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




