
Figure shows a closed surface which intersects a conducting sphere. If a positive charge is placed at point P, find the sign of flux passing through the curved surface S.
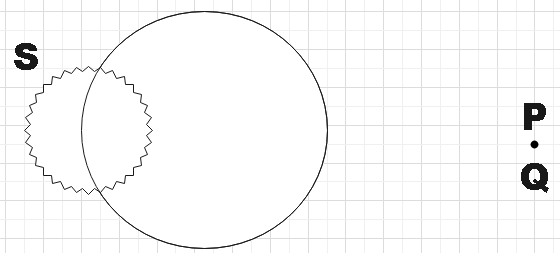

Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: As a first step we could recall the concept of induction of charge and then we could determine the charges induced as the result of introducing a charge Q at point P. Now, we could recall Gauss's law that gives the electric flux in terms of enclosed charge and thus determine the answer.
Formula used:
Gauss law,
$\phi =\oint{\overrightarrow{E}}\bullet \overrightarrow{dS}=\dfrac{{{q}_{enc}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, we are given a conducting sphere and a positive charge Q is placed at point P. We are supposed to find the sign of the flux passing through the curved surface S that intersects the given conducting sphere.
We have basic understanding of electrostatics to know that by keeping a charge in the vicinity of a conducting sphere will induce charge on the surface of the sphere. So, on the half that faces the point P will have the charge opposite to that of Q induced and other half will have positive charge induced as a further consequence. So, the charge distribution would now look like,
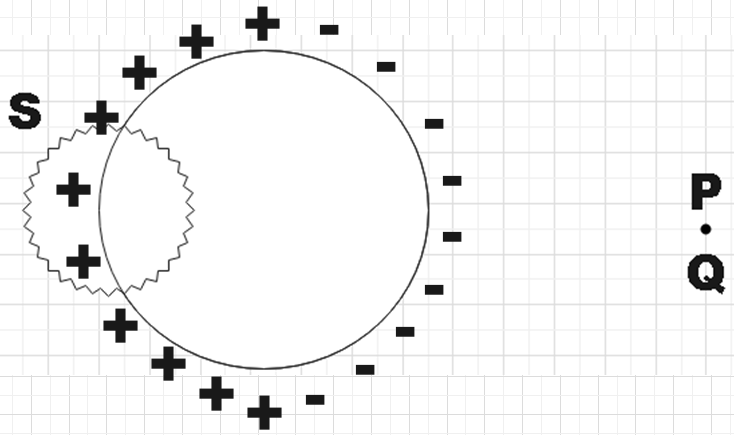
We know by Gauss’s law that electric flux is given by,
$\phi =\oint{\overrightarrow{E}}\bullet \overrightarrow{dS}=\dfrac{{{q}_{enc}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Also, from the figure we see that the charge enclosed in the surface S under consideration is positive and hence the resultant electric flux would also be positive.
Note: You may wonder how a charge can be introduced. Actually this concept of induction of charge follows the law of conservation of charge. You may see that one half of the surface has induced negative charge and as the result of this other half has positive charge on it. So, a new charge is created and the net charge still remains zero.
Formula used:
Gauss law,
$\phi =\oint{\overrightarrow{E}}\bullet \overrightarrow{dS}=\dfrac{{{q}_{enc}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, we are given a conducting sphere and a positive charge Q is placed at point P. We are supposed to find the sign of the flux passing through the curved surface S that intersects the given conducting sphere.
We have basic understanding of electrostatics to know that by keeping a charge in the vicinity of a conducting sphere will induce charge on the surface of the sphere. So, on the half that faces the point P will have the charge opposite to that of Q induced and other half will have positive charge induced as a further consequence. So, the charge distribution would now look like,

We know by Gauss’s law that electric flux is given by,
$\phi =\oint{\overrightarrow{E}}\bullet \overrightarrow{dS}=\dfrac{{{q}_{enc}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Also, from the figure we see that the charge enclosed in the surface S under consideration is positive and hence the resultant electric flux would also be positive.
Note: You may wonder how a charge can be introduced. Actually this concept of induction of charge follows the law of conservation of charge. You may see that one half of the surface has induced negative charge and as the result of this other half has positive charge on it. So, a new charge is created and the net charge still remains zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




