
Figure shows a balanced Wheatstone bridge. Now it is disturbed by changing P to $11\omega $. Which of the following steps will not bring the bridge to balance again?
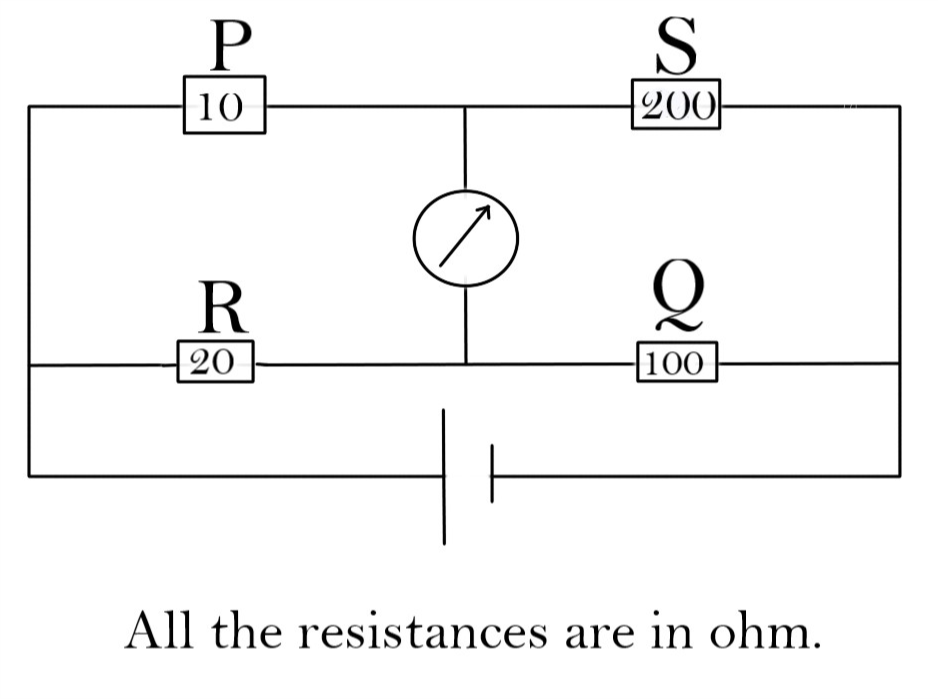
A. Increasing R by $2\Omega $
B. Increasing S by $20\Omega $
C. Increasing Q by $10\Omega $
D. Making product $RQ = 2200({\Omega ^2})$

Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: Make use of the concept of a balanced Wheatstone bridge.
Step by step answer:
If we increase the value of P from $10\Omega $ to $11\Omega $ then, either P or Q should be increased or S should be decreased. Hence increasing s by any amount will not result in the balancing of the bridge in any way.
We know that,
According to Wheatstone principle,
$\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{R}{S}$
$PS = RQ$
If we calculate RQ for this circuit,
$RQ = 2200{\Omega ^2}$
So, the equation becomes,
$PS = RQ = 2200{\Omega ^2}$
b) is correct
Additional information:
The device used for the measurement of minimum resistance with the help of comparison method is known as the Wheatstone bridge. The value of unknown resistance is determined by comparing it with the known resistance. The Wheatstone bridge works on the principle of null deflection, i.e. the ratio of their resistances are equal, and no current flows through the galvanometer. The bridge is very reliable and gives an accurate result.
Note: If we replace the resistances in the opposite branches with each other than the Wheatstone bridge still remains balanced and it still holds the Wheatstone’s law.
Step by step answer:
If we increase the value of P from $10\Omega $ to $11\Omega $ then, either P or Q should be increased or S should be decreased. Hence increasing s by any amount will not result in the balancing of the bridge in any way.
We know that,
According to Wheatstone principle,
$\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{R}{S}$
$PS = RQ$
If we calculate RQ for this circuit,
$RQ = 2200{\Omega ^2}$
So, the equation becomes,
$PS = RQ = 2200{\Omega ^2}$
b) is correct
Additional information:
The device used for the measurement of minimum resistance with the help of comparison method is known as the Wheatstone bridge. The value of unknown resistance is determined by comparing it with the known resistance. The Wheatstone bridge works on the principle of null deflection, i.e. the ratio of their resistances are equal, and no current flows through the galvanometer. The bridge is very reliable and gives an accurate result.
Note: If we replace the resistances in the opposite branches with each other than the Wheatstone bridge still remains balanced and it still holds the Wheatstone’s law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




