
Fertilisation takes place in
(a) Fallopian tube
(b) Follicle
(c) Uterus
(d) Vagina
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The ovum is released from the ovary and is transported by a long slender canal where it encounters sperm and they fuse, giving birth to a diploid unicellular zygote. This process is known as fertilisation.
Complete step by step answer:
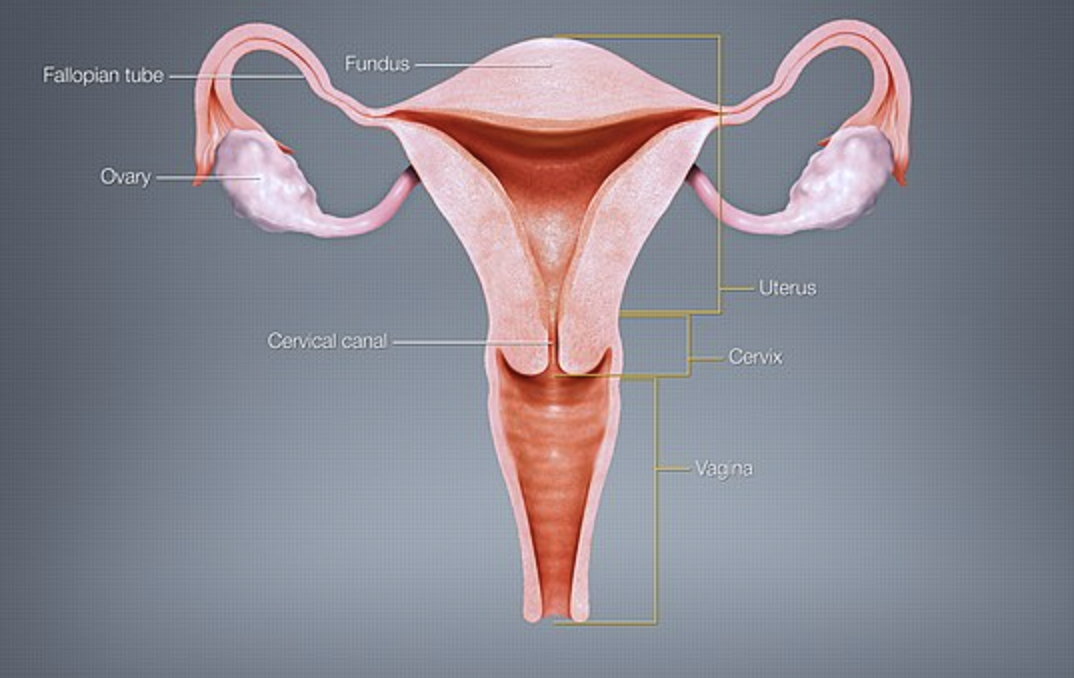
The process of fusion of a male gamete (or sperms) with a female gamete (ovum) is called fertilization. The two haploid nuclei each from either parent fuses to form a diploid zygote which is universal in all sexually reproducing organisms. Fertilisation occurs in the isthmus portion of the fallopian tube. After fertilisation, a series of rapid mitotic divisions called cleavage takes place. In humans, cleavage begins in the fallopian tube and morula is achieved after the 4th day of fertilisation.
Additional Information:
- Cleavage transforms the zygote into a morula. It is characterised by a solid mass of cells with 16- 32 cells.
- This will lead to a blastula stage or hollow mass of cells. A fluid- filled cavity inside the ball of cells is called the blastocoel surrounded by an outer layer ‘trophoblast’ and an inner layer ‘inner cell mass.’
- The trophoblast layer extends into the endometrial lining of the uterus by breaking down the molecules of the endometrium.
- This is then followed by the gastrulation stage wherein the three germ layers are originated by the rearrangement of cells into endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. And this ball of cells is known as gastrula.
- After implantation, the placenta is formed.
- Ovarian follicles are small sac- like structures filled with fluid and enclosing a growing oocyte or immature ovum or egg cell.
- Uterus serves as the pathway for sperm deposited in the vagina to reach the uterine tubes or fallopian tubes.
- Vagina is a tubular and a 10 cm long canal lined with a mucous membrane extending from the exterior of the body to the uterine cervix.
So, the correct answer is ‘Fallopian tubes.’
Note: The placenta acts as a barrier between the foetus and the mother. Although the blood of foetus and mother do not mix or blend, the placenta acts as an ultrafilter where soluble nutrients, minerals, hormones, antibodies, can cross over and pass onto the foetus. It also helps in the exchange of gases between the two as well as the elimination of nitrogenous wastes from the foetus.
Complete step by step answer:
The process of fusion of a male gamete (or sperms) with a female gamete (ovum) is called fertilization. The two haploid nuclei each from either parent fuses to form a diploid zygote which is universal in all sexually reproducing organisms. Fertilisation occurs in the isthmus portion of the fallopian tube. After fertilisation, a series of rapid mitotic divisions called cleavage takes place. In humans, cleavage begins in the fallopian tube and morula is achieved after the 4th day of fertilisation.
Additional Information:
- Cleavage transforms the zygote into a morula. It is characterised by a solid mass of cells with 16- 32 cells.

- This will lead to a blastula stage or hollow mass of cells. A fluid- filled cavity inside the ball of cells is called the blastocoel surrounded by an outer layer ‘trophoblast’ and an inner layer ‘inner cell mass.’
- The trophoblast layer extends into the endometrial lining of the uterus by breaking down the molecules of the endometrium.
- This is then followed by the gastrulation stage wherein the three germ layers are originated by the rearrangement of cells into endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. And this ball of cells is known as gastrula.
- After implantation, the placenta is formed.
- Ovarian follicles are small sac- like structures filled with fluid and enclosing a growing oocyte or immature ovum or egg cell.
- Uterus serves as the pathway for sperm deposited in the vagina to reach the uterine tubes or fallopian tubes.
- Vagina is a tubular and a 10 cm long canal lined with a mucous membrane extending from the exterior of the body to the uterine cervix.
So, the correct answer is ‘Fallopian tubes.’
Note: The placenta acts as a barrier between the foetus and the mother. Although the blood of foetus and mother do not mix or blend, the placenta acts as an ultrafilter where soluble nutrients, minerals, hormones, antibodies, can cross over and pass onto the foetus. It also helps in the exchange of gases between the two as well as the elimination of nitrogenous wastes from the foetus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




