
What is false about tRNA?
A. It binds with an amino acid at 5' end.
B. It has five base pairs stem
C. It has anticodon at one end which recognizes the codon on m-RNA
D. It looks like clover leaf in the two dimensional structure
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Transfer RNA or tRNA, is one of the types of a nucleic acid family known as ribonucleic acid (RNA). The function of tRNA molecules is to decode a messenger RNA (mRNA) that helps to translate genes and transfer into a sequence of proteins.
Complete answer:
The tRNA molecule has a distinctive folded two dimensional structure with three hairpin loops that looks like cloverleaf.
The primary structure of tRNA contains the modified bases; dihydrouridine, ribothymidine, pseudouridine and inosine.
The amino acid binds with the sequence of CCA tail (cytosine-cytosine-adenine) at the 3' end of the tRNA molecule.
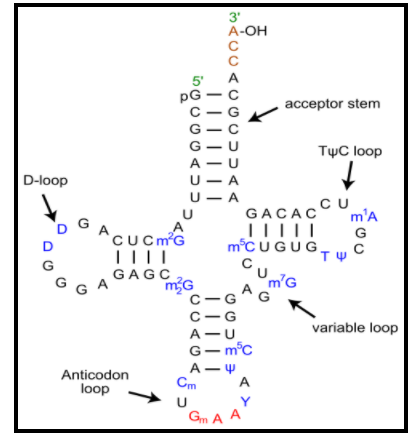
The cloverleaf molecular structure of tRNA, being the shape of a three-leafed clover, is composed of three characteristic loops such as anticodon, a D-arm and a T-arm.
As shown in the given figure above, the D arm is the loop closest to the 5' end and it often contains dihydrouridine bases.
The loop that contains the sequence of thymine-pseudouridine-cytosine lying closest to the 3' end is called the T arm.
The anticodon arm is a 5-bp stem whose loop found on the bottom of the cloverleaf structure contains the anticodon. The primary function of anticodon in t-RNA is to recognize and decode m-RNA codons
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: The molecules of Transfer RNAs or tRNAs act as temporary carriers between nucleotide and amino acid sequences. Its primary function is to bring up the appropriate amino acids to the ribosome by decoding the nucleotide sequence of the messenger RNA (mRNA). In this way, they act as the intermediaries in order to synthesize a protein from an mRNA molecule.
Complete answer:
The tRNA molecule has a distinctive folded two dimensional structure with three hairpin loops that looks like cloverleaf.
The primary structure of tRNA contains the modified bases; dihydrouridine, ribothymidine, pseudouridine and inosine.
The amino acid binds with the sequence of CCA tail (cytosine-cytosine-adenine) at the 3' end of the tRNA molecule.

The cloverleaf molecular structure of tRNA, being the shape of a three-leafed clover, is composed of three characteristic loops such as anticodon, a D-arm and a T-arm.
As shown in the given figure above, the D arm is the loop closest to the 5' end and it often contains dihydrouridine bases.
The loop that contains the sequence of thymine-pseudouridine-cytosine lying closest to the 3' end is called the T arm.
The anticodon arm is a 5-bp stem whose loop found on the bottom of the cloverleaf structure contains the anticodon. The primary function of anticodon in t-RNA is to recognize and decode m-RNA codons
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: The molecules of Transfer RNAs or tRNAs act as temporary carriers between nucleotide and amino acid sequences. Its primary function is to bring up the appropriate amino acids to the ribosome by decoding the nucleotide sequence of the messenger RNA (mRNA). In this way, they act as the intermediaries in order to synthesize a protein from an mRNA molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




