
Fac and Mer isomerism is associated with which of the following general formulas?
A. $[M{(AA)_2}]$
B. $[M{(AA)_3}]$
C. $[MABCD]$
D. $[M{A_3}{B_3}]$
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: First we need to understand the basics of geometrical isomerism. After that, we can easily differentiate between a fac-isomer and a mer-isomer. Geometrical isomerism is a type of isomerism that is generally observed in heteroleptic complexes.
Complete step by step answer:
Geometrical isomerism occurs due to different feasible geometrical arrangements of the ligands. When the two same groups engage adjacent positions, then the isomer is called cis-isomer, and when they are arranged opposite to one another, then the isomer is called trans-isomer.
As we know that the octahedral complexes also show cis and trans-isomerism due to the difference in the spatial arrangements of the ligands.
In cis-form, when similar groups utilize adjacent positions at the corners of one of the octahedral faces then it is known as facial or fac-isomer while in trans-form, when the position of a donor atom is around the meridian of the octahedron then it is known as meridian or mer-isomer.
Now, we will refer to the formula of the compound to check which of these will exhibit both fac and mer-isomerism.
For the formula, $[M{A_3}{B_3}]$ there are three A ligands present on one side of the triangular face and three B ligands that are present on the opposite side of the triangular face. Thus, it exhibits both Fac and mer-isomers.
Now, let’s draw the fac and mer-isomerism structure of the following formula $MA_3B_3$
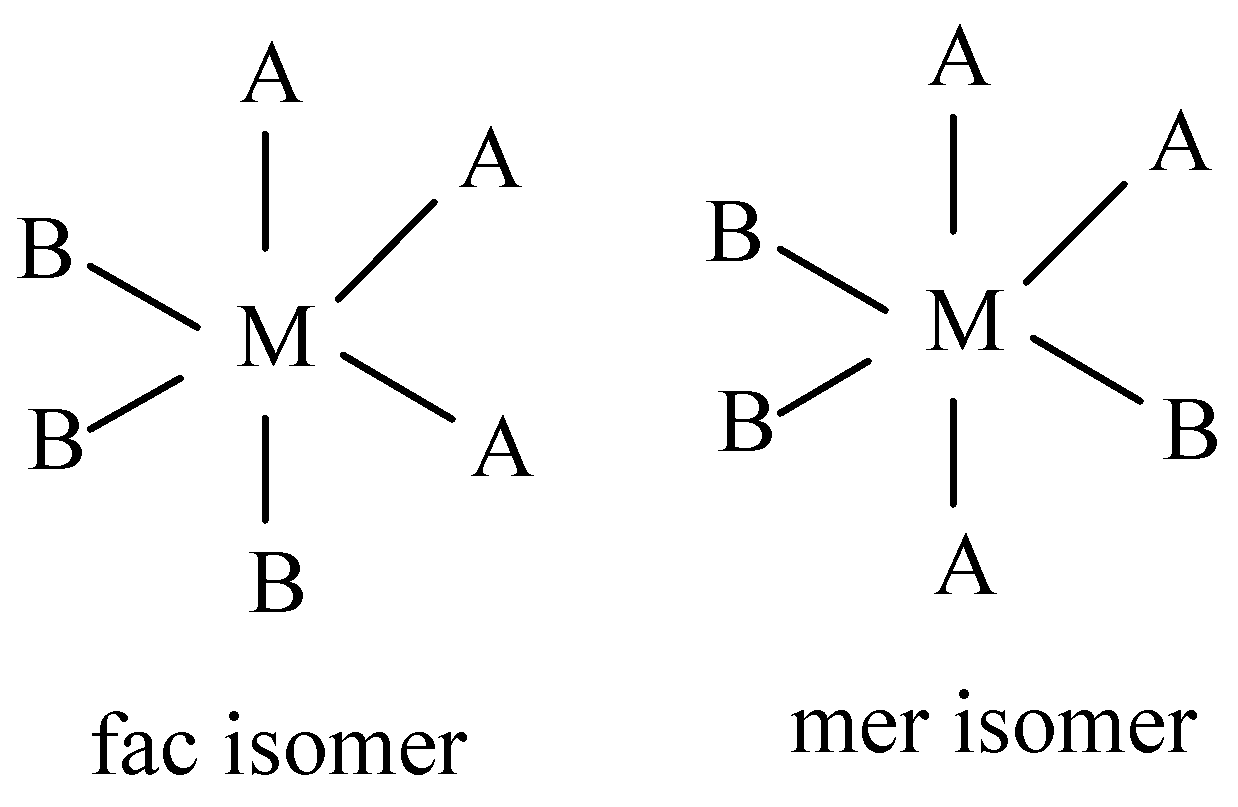
And hence the correct option is D.
Note:
We must know that the geometrical isomers are molecules that are packed in spatial arrangements with respect to one another due to the occurrence or rising of a ring structure or a double bond.
Complete step by step answer:
Geometrical isomerism occurs due to different feasible geometrical arrangements of the ligands. When the two same groups engage adjacent positions, then the isomer is called cis-isomer, and when they are arranged opposite to one another, then the isomer is called trans-isomer.
As we know that the octahedral complexes also show cis and trans-isomerism due to the difference in the spatial arrangements of the ligands.
In cis-form, when similar groups utilize adjacent positions at the corners of one of the octahedral faces then it is known as facial or fac-isomer while in trans-form, when the position of a donor atom is around the meridian of the octahedron then it is known as meridian or mer-isomer.
Now, we will refer to the formula of the compound to check which of these will exhibit both fac and mer-isomerism.
For the formula, $[M{A_3}{B_3}]$ there are three A ligands present on one side of the triangular face and three B ligands that are present on the opposite side of the triangular face. Thus, it exhibits both Fac and mer-isomers.
Now, let’s draw the fac and mer-isomerism structure of the following formula $MA_3B_3$

And hence the correct option is D.
Note:
We must know that the geometrical isomers are molecules that are packed in spatial arrangements with respect to one another due to the occurrence or rising of a ring structure or a double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




