
How would you explain what a \[1,2 - \] alkyl shift is?
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: We need to remember that the \[1,2 - \]alkyl shift is a type of carbocation rearrangement reaction which is very common in organic chemistry. We know that carbocation is formed in the organic reactions as a result of loss of two valence electrons. It is an intermediate and positively charged entity. These are unstable and undergo rearrangements like \[1,2 - \]alkyl shift and hydride shift to form stable carbocation. Reactivity order of carbocations is $3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ > methyl$ .
Complete step by step answer:
We need to know that the \[1,2 - \] alkyl shift is a shift of an alkyl group to an adjacent carbon atom of the same compound. It is also known as \[1,2 - \] methyl shift if the moving chemical species is methyl group or \[1,2 - \] ethyl shift if the moving chemical species is ethyl group. For eg.
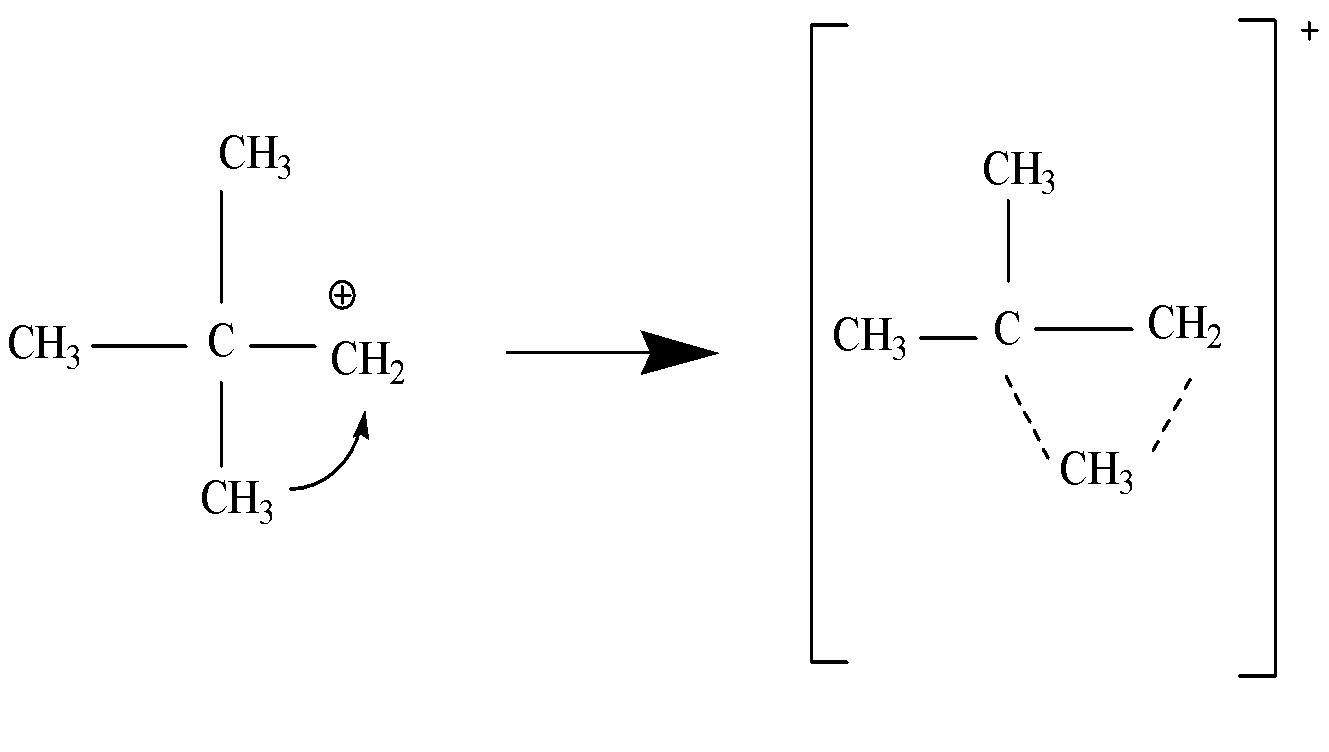
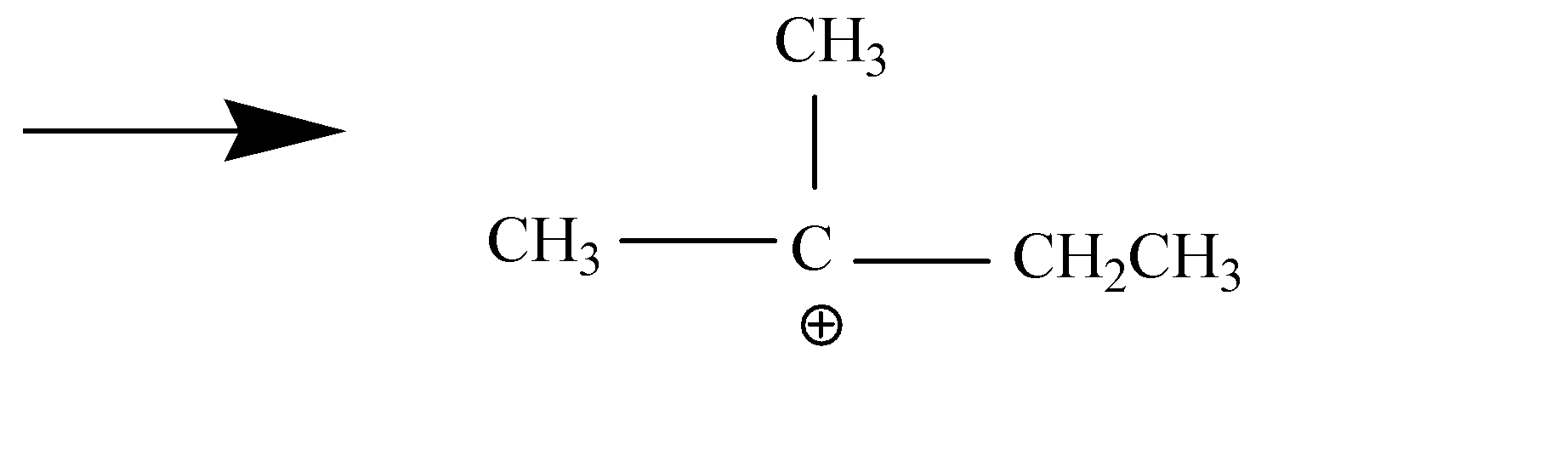
In the above example, we have carbocation, where we will move the plus charge to the carbon in the center to get stable carbocation, and for that we need to move the $C{H_3}$ group to $C{H_2}$ and that is called as \[1,2 - \] methyl shift and we will get a transition state which further result into a carbocation and is more stable than the initial one. This occurs due to hyperconjugation from electron donating groups. It should be noted that there is no hydrogen on the center carbon so there will be no hydride shift.
Note:
The rule to remember is the alkyl group which shifts is the smaller one. \[1,2 - \] alkyl shift is a type of nucleophilic rearrangement and is intramolecular (between the same compound). Most common example of this type of shift is Pinacol rearrangement reaction.Another type of carbocation rearrangement is hydride shift which involves the movement of hydrogen atom from one carbon to another adjacent atom and this is little bit faster than methyl shift.
Complete step by step answer:
We need to know that the \[1,2 - \] alkyl shift is a shift of an alkyl group to an adjacent carbon atom of the same compound. It is also known as \[1,2 - \] methyl shift if the moving chemical species is methyl group or \[1,2 - \] ethyl shift if the moving chemical species is ethyl group. For eg.


In the above example, we have carbocation, where we will move the plus charge to the carbon in the center to get stable carbocation, and for that we need to move the $C{H_3}$ group to $C{H_2}$ and that is called as \[1,2 - \] methyl shift and we will get a transition state which further result into a carbocation and is more stable than the initial one. This occurs due to hyperconjugation from electron donating groups. It should be noted that there is no hydrogen on the center carbon so there will be no hydride shift.
Note:
The rule to remember is the alkyl group which shifts is the smaller one. \[1,2 - \] alkyl shift is a type of nucleophilic rearrangement and is intramolecular (between the same compound). Most common example of this type of shift is Pinacol rearrangement reaction.Another type of carbocation rearrangement is hydride shift which involves the movement of hydrogen atom from one carbon to another adjacent atom and this is little bit faster than methyl shift.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




