
Explain the significance of Lenz’s law to show the conservation of energy.
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint:To answer this question, we need to consider the Faraday’s experiment. There we need to examine the law of conservation of energy.
Complete step-by-step solution
Lenz's law states that the polarity of emf induced in a circuit, which is subjected to changing magnetic field, is such that it produces a current which opposes the change in magnetic flux, due to which it is produced.
It is reflected in Faraday’s law by the negative sign as written below
\[e = - \dfrac{{d\varphi }}{{dt}}\]
Lenz's law is basically based on the law of conservation of energy. Consider a situation, where the north pole of the magnet is brought towards a circular conducting loop.
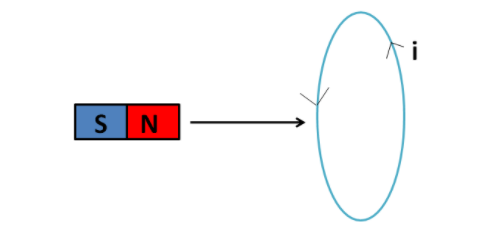
In this case, according to Lenz's law, the emf induced in the loop will be such that the current produced will oppose the change in magnetic flux through the loop. So, the current induced will be counter-clockwise, as shown in the above figure. So, the north pole of the magnet will face the north pole of the loop, due to which force of repulsion will be there.
If we assume that the direction of the current induced in the loop opposite to that according to Lenz's law, i.e. in the clockwise direction, then the north pole of the magnet would face the south pole of the loop, due to which the magnet would get attracted to the loop. This means that if we would give a slight push to the magnet towards the loop, the current in the loop would be set up such that it would start attracting the magnet, thereby increasing its energy. But this is a violation of the principle of energy conservation.
Hence, Lenz's law puts a restriction of the conservation of energy principle on the polarity of the induced emf.
Note: We could argue that where is the kinetic energy going which is provided to the magnet externally, because the repulsion from the loop will decrease its energy. The explanation is that it is dissipated in the form of heat in the loop.
Complete step-by-step solution
Lenz's law states that the polarity of emf induced in a circuit, which is subjected to changing magnetic field, is such that it produces a current which opposes the change in magnetic flux, due to which it is produced.
It is reflected in Faraday’s law by the negative sign as written below
\[e = - \dfrac{{d\varphi }}{{dt}}\]
Lenz's law is basically based on the law of conservation of energy. Consider a situation, where the north pole of the magnet is brought towards a circular conducting loop.

In this case, according to Lenz's law, the emf induced in the loop will be such that the current produced will oppose the change in magnetic flux through the loop. So, the current induced will be counter-clockwise, as shown in the above figure. So, the north pole of the magnet will face the north pole of the loop, due to which force of repulsion will be there.
If we assume that the direction of the current induced in the loop opposite to that according to Lenz's law, i.e. in the clockwise direction, then the north pole of the magnet would face the south pole of the loop, due to which the magnet would get attracted to the loop. This means that if we would give a slight push to the magnet towards the loop, the current in the loop would be set up such that it would start attracting the magnet, thereby increasing its energy. But this is a violation of the principle of energy conservation.
Hence, Lenz's law puts a restriction of the conservation of energy principle on the polarity of the induced emf.
Note: We could argue that where is the kinetic energy going which is provided to the magnet externally, because the repulsion from the loop will decrease its energy. The explanation is that it is dissipated in the form of heat in the loop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




