
Explain the refraction of light through a glass slab with a neat ray diagram .
Answer
570.3k+ views
Hint: Before proceeding with the complete solution of the given question, we need to primarily get brushed up with the Laws of refraction of light which are:
1. The incident ray refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
2. The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant i.e. $\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\mu $
Complete step by step answer:
Consider the rectangular glass slab PQRS in which refraction of light through a glass slab shall be explained.
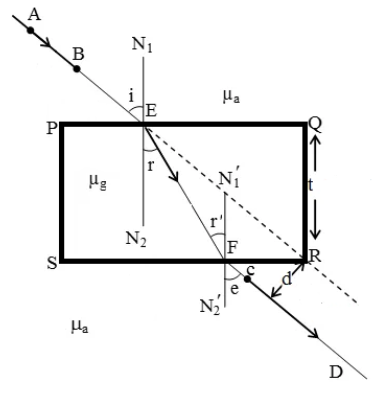
When an incident ray of light AB passes from a rarer medium (air) to a denser medium (glass) at point E on the interface of the two media PQ, it will bends towards the normal as we know, rays coming from rarer medium to denser medium bends towards the normal.
Again at point F, on the interface SR the light ray proceeds from denser medium (glass) to the rarer medium (air), where the light ray shall bend away from normal, resultantly, EF and CD being the refracted ray and the emergent ray respectively.
Now, if the incident ray is extended to the interface SR, it shall be observed that emergent ray CD becomes parallel to the incident ray AB, the reason being that both the rays are travelling in the same medium, hence equal velocity.
The emergent ray shall also be slightly laterally displaced after refraction and the factors that this lateral displacement depends on are: thickness of the glass slab, refractive index of the glass slab and the angle at which incident ray enters the glass slab.
Note: One is advised to remember that there exists a case where there is no net lateral displacement and this occurs when a ray of light is incident normally to the interface of the two media, passing the rectangular glass slab straight away without any deviation.
1. The incident ray refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
2. The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant i.e. $\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\mu $
Complete step by step answer:
Consider the rectangular glass slab PQRS in which refraction of light through a glass slab shall be explained.

When an incident ray of light AB passes from a rarer medium (air) to a denser medium (glass) at point E on the interface of the two media PQ, it will bends towards the normal as we know, rays coming from rarer medium to denser medium bends towards the normal.
Again at point F, on the interface SR the light ray proceeds from denser medium (glass) to the rarer medium (air), where the light ray shall bend away from normal, resultantly, EF and CD being the refracted ray and the emergent ray respectively.
Now, if the incident ray is extended to the interface SR, it shall be observed that emergent ray CD becomes parallel to the incident ray AB, the reason being that both the rays are travelling in the same medium, hence equal velocity.
The emergent ray shall also be slightly laterally displaced after refraction and the factors that this lateral displacement depends on are: thickness of the glass slab, refractive index of the glass slab and the angle at which incident ray enters the glass slab.
Note: One is advised to remember that there exists a case where there is no net lateral displacement and this occurs when a ray of light is incident normally to the interface of the two media, passing the rectangular glass slab straight away without any deviation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




