
Explain the polar covalent bond with the help of a suitable example.
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: Consider the electronegativity difference between two atoms joined by covalent bond. When two atoms have significant electronegativity difference, the bond pair of electrons is unequally shared between two atoms and the bond is a polar covalent bond.
Complete answer:
Polar covalent bond is formed between two atoms having different electronegativities. The shared pair of electrons is unequally distributed between two atoms. The shared pair of electrons is more attracted by the more electronegative atom.
Greater is the difference in electro-negativity of two atoms, greater is the polarity of the bond. For example, the bond between hydrogen atom and chlorine atom is a polar covalent bond. Its structure is as shown below:
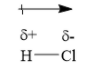
Consider the covalent bond formed between one hydrogen atom and one chlorine atom of hydrogen chloride molecule. This bond is a polar covalent bond. Chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen. The bond pair of electrons will be more attracted towards more electronegative chlorine atom. Bond pair of electrons will not be present at the midpoint between hydrogen and chlorine atom. The bond pair of electrons will be away from the hydrogen atom and closer towards chlorine atoms. Due to this, chlorine atom gains partial negative charge and hydrogen atom gains partial positive charge. Due to this, the hydrogen chloride molecule becomes polar and has a dipole moment.
The bond between nitrogen and hydrogen atoms of ammonia molecules is also a polar covalent bond. The bond between oxygen and hydrogen atom of water molecule is also a polar covalent bond.
When a covalent bond is present between two atoms of the same element, the electronegativity difference is zero and the bond is a nonpolar covalent bond. The bond between two hydrogen atoms of hydrogen molecule is a nonpolar covalent bond. Similarly, the bond between two chlorine atoms of chlorine molecule is a nonpolar covalent bond.
Note: The electronegativity difference between two bonds should not be too high as the bond will lose its covalent nature and will become ionic bond.
Complete answer:
Polar covalent bond is formed between two atoms having different electronegativities. The shared pair of electrons is unequally distributed between two atoms. The shared pair of electrons is more attracted by the more electronegative atom.
Greater is the difference in electro-negativity of two atoms, greater is the polarity of the bond. For example, the bond between hydrogen atom and chlorine atom is a polar covalent bond. Its structure is as shown below:
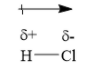
Consider the covalent bond formed between one hydrogen atom and one chlorine atom of hydrogen chloride molecule. This bond is a polar covalent bond. Chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen. The bond pair of electrons will be more attracted towards more electronegative chlorine atom. Bond pair of electrons will not be present at the midpoint between hydrogen and chlorine atom. The bond pair of electrons will be away from the hydrogen atom and closer towards chlorine atoms. Due to this, chlorine atom gains partial negative charge and hydrogen atom gains partial positive charge. Due to this, the hydrogen chloride molecule becomes polar and has a dipole moment.
The bond between nitrogen and hydrogen atoms of ammonia molecules is also a polar covalent bond. The bond between oxygen and hydrogen atom of water molecule is also a polar covalent bond.
When a covalent bond is present between two atoms of the same element, the electronegativity difference is zero and the bond is a nonpolar covalent bond. The bond between two hydrogen atoms of hydrogen molecule is a nonpolar covalent bond. Similarly, the bond between two chlorine atoms of chlorine molecule is a nonpolar covalent bond.
Note: The electronegativity difference between two bonds should not be too high as the bond will lose its covalent nature and will become ionic bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




