
Explain the nutrition in the pitcher plant with a diagram.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Pitcher plant has a partial heterotrophic mode of nutrition. To sustain its nitrogenous requirement, it nurtures insects as pitcher plants grow in nitrogen-lacking soil.
Complete answer:
The term 'partially heterotrophic' is used for insectivorous plants. They have chlorophyll and are capable of carrying out photosynthesis but they depend on some of the nutrients (like nitrogen) on other organisms.
The pitcher plant is insectivorous. It grows in nitrogen-deficient soil so derives its nitrogen from insects.
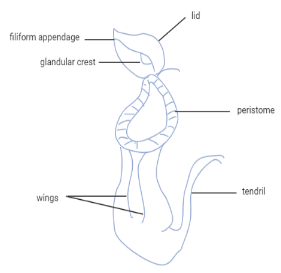
The leaf of the pitcher plant is changed to develop a pitcher-like shape. The bright color of the pitcher makes it very appealing to insects. Within the pitcher; there are numerous hair-like structures. These hairs lead the entrapped insects downwards
The lid of the pitcher shuts down once an insect lies on the pitcher of the plant and the insect gets entrapped inside the pitcher. After this, the insect then breaks down and is digested by the aid of enzymes produced by the cells of the plants.
The prey substances captured are then changed into a mixture of nitrogenous compounds from which the plant gains its mineral nutrition, mainly nitrogen and phosphorus.
So, the answer to the above question is that the mode of nutrition in the pitcher plant is partially heterotrophic nutrition.
Note: While answering the question always keep in mind that the pitcher plant grows in areas where the soil is lacking in minerals or excessively acidic for most plants to live.
Complete answer:
The term 'partially heterotrophic' is used for insectivorous plants. They have chlorophyll and are capable of carrying out photosynthesis but they depend on some of the nutrients (like nitrogen) on other organisms.
The pitcher plant is insectivorous. It grows in nitrogen-deficient soil so derives its nitrogen from insects.
The leaf of the pitcher plant is changed to develop a pitcher-like shape. The bright color of the pitcher makes it very appealing to insects. Within the pitcher; there are numerous hair-like structures. These hairs lead the entrapped insects downwards
The lid of the pitcher shuts down once an insect lies on the pitcher of the plant and the insect gets entrapped inside the pitcher. After this, the insect then breaks down and is digested by the aid of enzymes produced by the cells of the plants.
The prey substances captured are then changed into a mixture of nitrogenous compounds from which the plant gains its mineral nutrition, mainly nitrogen and phosphorus.
So, the answer to the above question is that the mode of nutrition in the pitcher plant is partially heterotrophic nutrition.

Note: While answering the question always keep in mind that the pitcher plant grows in areas where the soil is lacking in minerals or excessively acidic for most plants to live.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




