
Explain the mechanism of acetaldehyde involved in crossed aldol condensation.
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: A crossed aldol condensation involving acetaldehyde will have acetaldehyde and any other carbonyl compound as reactants and they will form a mixture of products.
Complete step by step answer:
-When aldol condensation is done between two different carbonyl compounds, it is known as crossed aldol condensation.
-This reaction is a nucleophilic addition reaction.
-Here, we have taken acetaldehyde and another aldehyde ${R_2}CH - CHO$ (where R is any alkyl group) as reactants. They both have $\alpha $- hydrogens. In the presence of a base like dilute sodium hydroxide, they will react to form at least four products, the two self-condensation products of the two aldehydes and the two cross aldol condensation products. The mechanism of the reactions in which the two cross aldol condensation products are obtained are given below:
In the first mechanism, the enolate ion of acetaldehyde attacks the carbonyl carbon of the other aldehyde. The product formed is a $\beta $-hydroxy aldehyde.
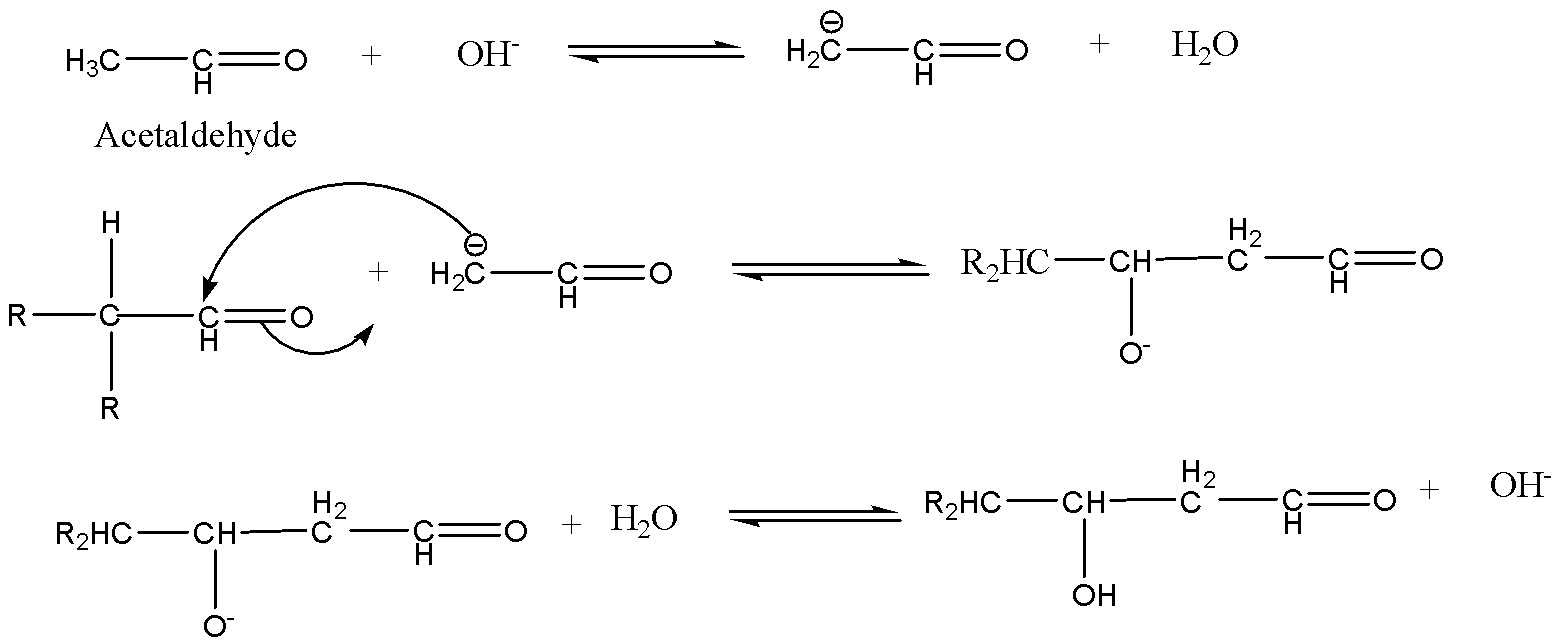
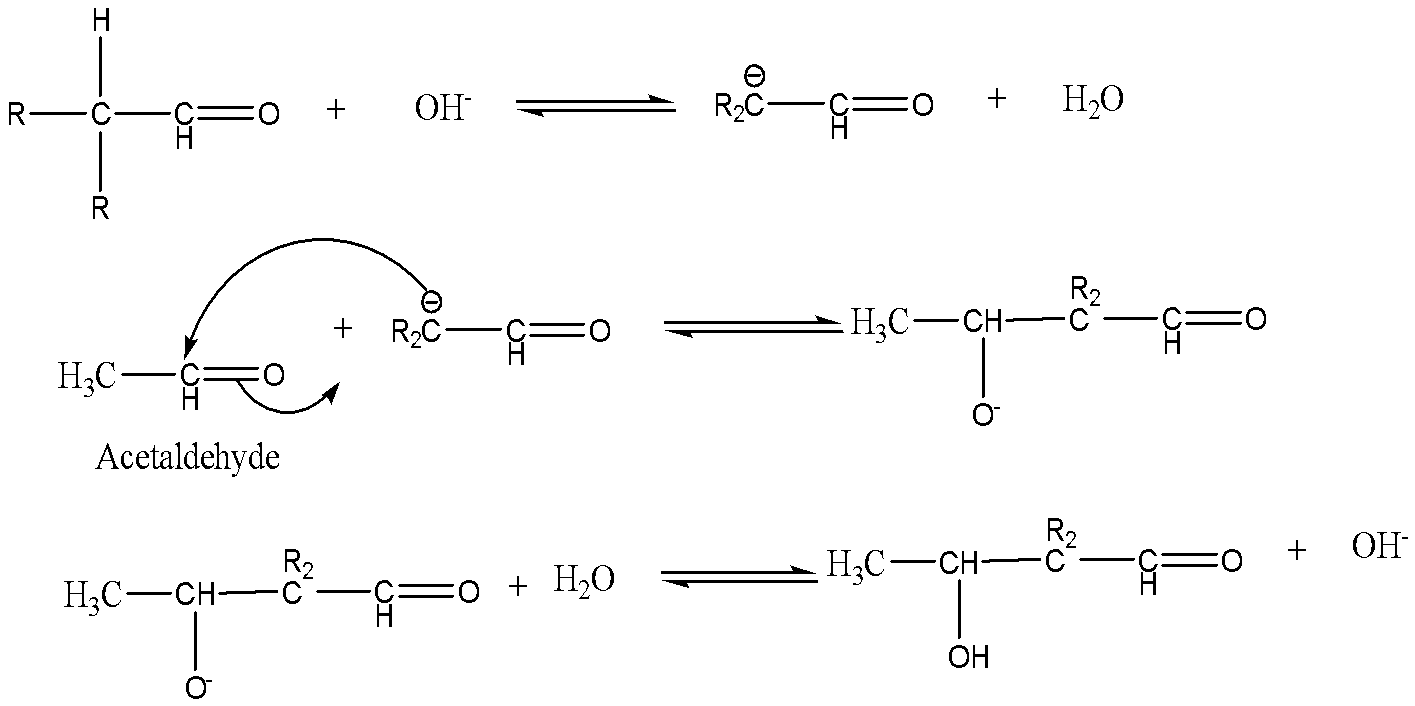
In the second mechanism, the enolate ion of the other aldehyde attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acetaldehyde. The product formed is a $\beta $-hydroxy aldehyde.
Note:
The above reactions are an example of a crossed aldol condensation between two different aldehydes both containing $\alpha $- hydrogen atoms form four products.But there also occurs crossed aldol condensation between two different aldehydes where one of the aldehyde has no $\alpha $- hydrogen atom $(e.g.\,{C_6}{H_5} - CHO)$. In such a case only two products are obtained (one crossed aldol and one self-aldol condensation product).
Complete step by step answer:
-When aldol condensation is done between two different carbonyl compounds, it is known as crossed aldol condensation.
-This reaction is a nucleophilic addition reaction.
-Here, we have taken acetaldehyde and another aldehyde ${R_2}CH - CHO$ (where R is any alkyl group) as reactants. They both have $\alpha $- hydrogens. In the presence of a base like dilute sodium hydroxide, they will react to form at least four products, the two self-condensation products of the two aldehydes and the two cross aldol condensation products. The mechanism of the reactions in which the two cross aldol condensation products are obtained are given below:
In the first mechanism, the enolate ion of acetaldehyde attacks the carbonyl carbon of the other aldehyde. The product formed is a $\beta $-hydroxy aldehyde.

In the second mechanism, the enolate ion of the other aldehyde attacks the carbonyl carbon of the acetaldehyde. The product formed is a $\beta $-hydroxy aldehyde.

Note:
The above reactions are an example of a crossed aldol condensation between two different aldehydes both containing $\alpha $- hydrogen atoms form four products.But there also occurs crossed aldol condensation between two different aldehydes where one of the aldehyde has no $\alpha $- hydrogen atom $(e.g.\,{C_6}{H_5} - CHO)$. In such a case only two products are obtained (one crossed aldol and one self-aldol condensation product).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




