
Explain the following : $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ is a weak acid.
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$ is an organic compound belonging to the class of carboxylic acids. Try to compare the conjugate base of ethanoic acid and conjugate base of a mineral acid. Stronger the conjugate base, weaker is the acid. You can find out the ${{K}_{a}}$ value for ethanoic acid to support your observations.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In chemistry, organic compounds are chemical compounds containing carbon-hydrogen bonds in simple terms. Along with carbon and hydrogen, organic compounds contain atoms like oxygen, nitrogen and halogens( Cl, Br ,I, F).
The study of properties, reactions and their mechanisms and their synthesis is known as organic chemistry. Till now we have found and synthesised millions of organic compounds due to the catenation property of carbon.
The general formula for the class of organic compounds given above has a -COOH group. The compounds having a -COOH group at the terminal, belong to the class of carboxylic acids.
We will now discuss the acidic nature of ethanoic acid and why it is referred to as weak acid.
Organic acids are in general considered to be weak acids due to relatively less stable conjugate base in comparison to a mineral acid.
The structure of ethanoic acid is :

Upon deprotonation, the conjugate base of ethanoic acid becomes:
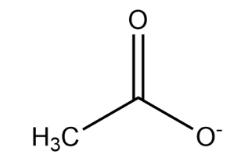
In the above structure, there is resonance between the two oxygen atoms attached to the carbon atom which stabilises the negative charge. However, the methyl group increases electron density on the carbon atom making the resonating structure unstable. This is the reason why ethanoic acid is considered to be a weak acid.
Note: For historical reasons, some classes of organic compounds like carbonates, anion salts, cyanide salts and carbon dioxide are not considered organic compounds. They come under the class of inorganic compounds.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In chemistry, organic compounds are chemical compounds containing carbon-hydrogen bonds in simple terms. Along with carbon and hydrogen, organic compounds contain atoms like oxygen, nitrogen and halogens( Cl, Br ,I, F).
The study of properties, reactions and their mechanisms and their synthesis is known as organic chemistry. Till now we have found and synthesised millions of organic compounds due to the catenation property of carbon.
The general formula for the class of organic compounds given above has a -COOH group. The compounds having a -COOH group at the terminal, belong to the class of carboxylic acids.
We will now discuss the acidic nature of ethanoic acid and why it is referred to as weak acid.
Organic acids are in general considered to be weak acids due to relatively less stable conjugate base in comparison to a mineral acid.
The structure of ethanoic acid is :

Upon deprotonation, the conjugate base of ethanoic acid becomes:

In the above structure, there is resonance between the two oxygen atoms attached to the carbon atom which stabilises the negative charge. However, the methyl group increases electron density on the carbon atom making the resonating structure unstable. This is the reason why ethanoic acid is considered to be a weak acid.
Note: For historical reasons, some classes of organic compounds like carbonates, anion salts, cyanide salts and carbon dioxide are not considered organic compounds. They come under the class of inorganic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




