
Explain the energy pyramid.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: An energy pyramid is used to visualize how energy moves through levels of an ecosystem and how much of that energy is available at each level. It is a type of ecological pyramid. It is also known as the trophic pyramid.
Complete answer:
- An energy pyramid is a graphical representation of the flow of energy through the organic matter in an ecosystem.
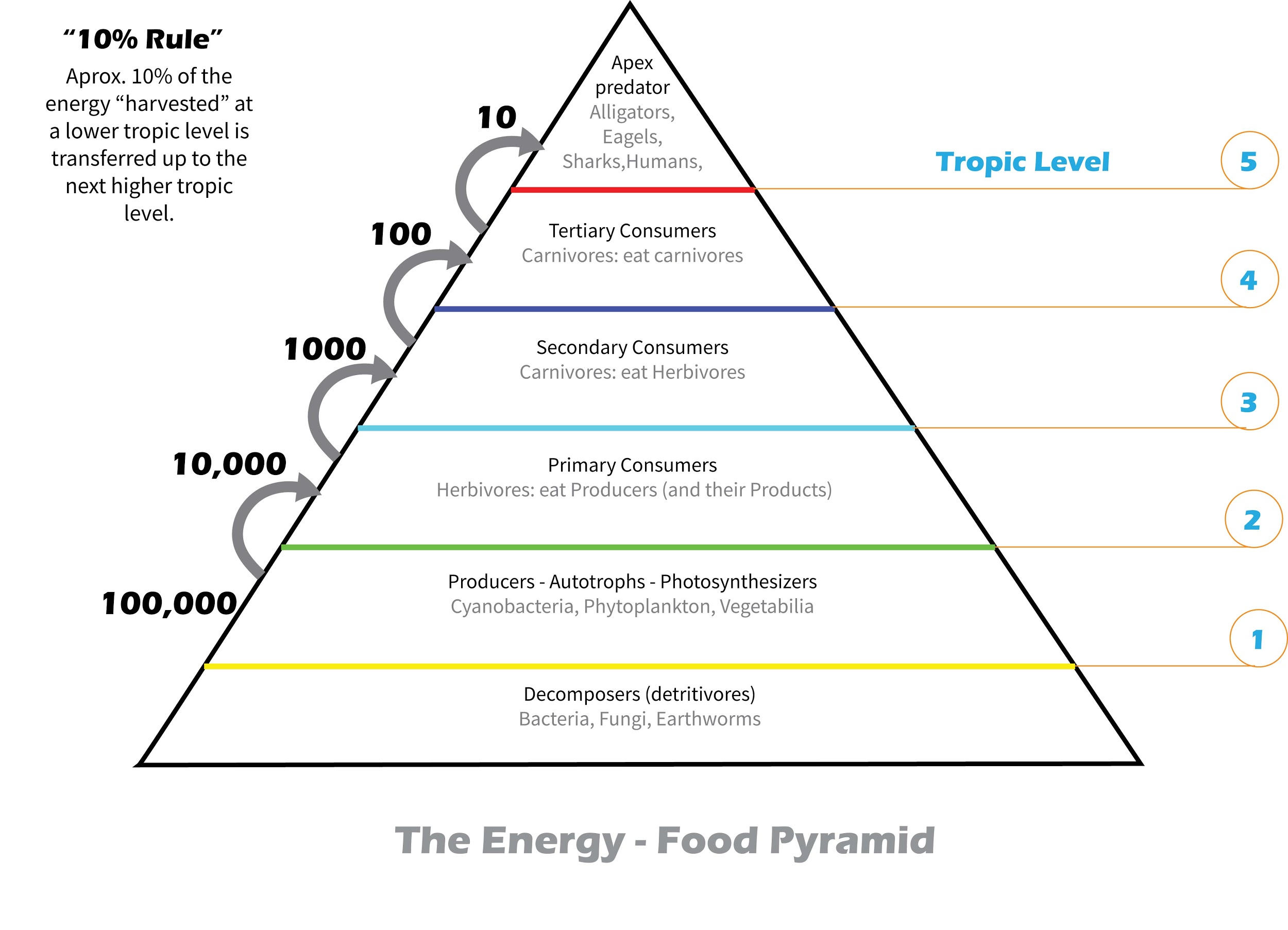
- The energy trapped per unit time and area in different levels of the food chain is expressed in it.
- In the Pyramid of energy the energy flow is unidirectional and thus it is always upright.
- Energy pyramids follow the 10% Rule.
- According to this rule when energy moves between trophic levels,10% of the energy is made available for the next level. The 90% is referred to as Metabolic loss.
- The trophic level that represents producers has the highest amount of energy.
- It follows that the carnivores (secondary consumers) that feed on herbivores and detritivores and those that eat other carnivores (tertiary consumers)have the lowest amount of energy available to them.
- Main disadvantage of the pyramid of energy is that it does not indicate the rate of biomass production. In some cases, it is difficult to assign organisms to a particular trophic level.
- Energy pyramids were proposed by Charles Elton.
- Using ecological pyramids, it is very easy to study the interaction between organisms.
Note:
There are 3 types of ecological pyramids
1. Pyramid of Number
2. Pyramid of Biomass
3. Pyramid of Energy
Pyramid of biomass is inverted in a pond ecosystem. The pyramid of numbers is inverted in the case of the parasitic food chain. It can be spindle- shaped also.
Complete answer:
- An energy pyramid is a graphical representation of the flow of energy through the organic matter in an ecosystem.

- The energy trapped per unit time and area in different levels of the food chain is expressed in it.
- In the Pyramid of energy the energy flow is unidirectional and thus it is always upright.
- Energy pyramids follow the 10% Rule.
- According to this rule when energy moves between trophic levels,10% of the energy is made available for the next level. The 90% is referred to as Metabolic loss.
- The trophic level that represents producers has the highest amount of energy.
- It follows that the carnivores (secondary consumers) that feed on herbivores and detritivores and those that eat other carnivores (tertiary consumers)have the lowest amount of energy available to them.
- Main disadvantage of the pyramid of energy is that it does not indicate the rate of biomass production. In some cases, it is difficult to assign organisms to a particular trophic level.
- Energy pyramids were proposed by Charles Elton.
- Using ecological pyramids, it is very easy to study the interaction between organisms.
Note:
There are 3 types of ecological pyramids
1. Pyramid of Number
2. Pyramid of Biomass
3. Pyramid of Energy
Pyramid of biomass is inverted in a pond ecosystem. The pyramid of numbers is inverted in the case of the parasitic food chain. It can be spindle- shaped also.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




