
Explain the difference between nucleoside and nucleotide.
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Nucleotide and nucleoside are the building blocks of nucleic acid (RNA and DNA). The nucleotides in the human DNA are arranged in a double-helical structure as shown in the Watson and Crick model.
Complete answer:
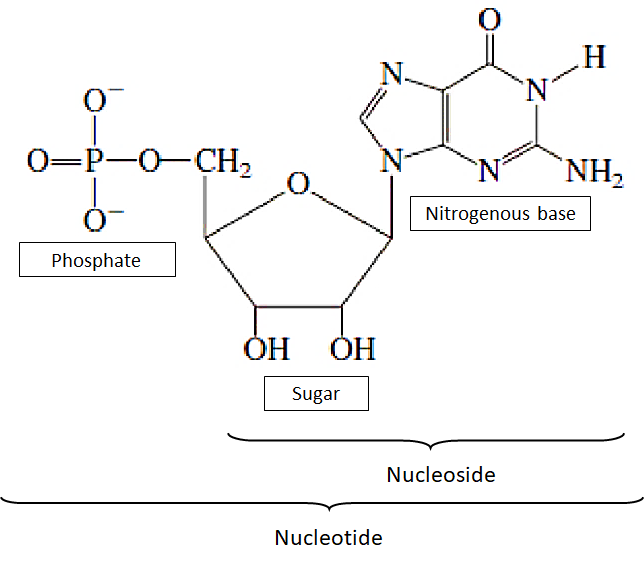
Nucleotides consist of the components such as a nitrogenous base, sugar, and a phosphate group while the nucleosides contain only sugar and a base. The nucleotide forms the basic structure of RNA and DNA, while the nucleoside occurs before the nucleotide itself.
Additional information:
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is composed of two polynucleotide chains arranged in a double-helical structure. It carries the genetic information for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all organisms and few viruses.
In DNA, there are four different bases- adenine (A) and guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and thymine (T). In RNA three of these are the same as in DNA: adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Instead of thymine (T) RNA consists of uracil (U).
Note: The biological functions of nucleotides are:
1. For data storage – The store the genetic information as part of DNA or RNA.
2. As energy currency – ATP or Adenosine Triphosphate is the basic unit of energy required to carry out all the functioning and processing in our body.
3. For cellular communication- cAMP, cGMP, etc. are used as secondary messengers for hormones and enzymes.
Complete answer:
Nucleotides consist of the components such as a nitrogenous base, sugar, and a phosphate group while the nucleosides contain only sugar and a base. The nucleotide forms the basic structure of RNA and DNA, while the nucleoside occurs before the nucleotide itself.
| Nucleoside | Nucleotide | |
| Chemical composition | A nucleoside consists of a nitrogenous base attached to a sugar(ribose or deoxyribose) with the help of a covalent bond. | A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, sugar(ribose or deoxyribose) and one to three phosphate groups |
| Relevance in medicine | Several nucleoside analogs are used as a treatment for viral disease or cancer. | Malfunctioning nucleotides are one of the main causes of all cancers known today. |
| Example | Examples of nucleosides include adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, uridine, and inosine. | Nucleotides have names complimentary to the nucleosides, but with the addition of phosphate groups. For example, 5’-uridine monophosphate. |
Additional information:
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is composed of two polynucleotide chains arranged in a double-helical structure. It carries the genetic information for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all organisms and few viruses.
In DNA, there are four different bases- adenine (A) and guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and thymine (T). In RNA three of these are the same as in DNA: adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Instead of thymine (T) RNA consists of uracil (U).
Note: The biological functions of nucleotides are:
1. For data storage – The store the genetic information as part of DNA or RNA.
2. As energy currency – ATP or Adenosine Triphosphate is the basic unit of energy required to carry out all the functioning and processing in our body.
3. For cellular communication- cAMP, cGMP, etc. are used as secondary messengers for hormones and enzymes.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




