
Explain the Carl Correns monohybrid cross in the Four O’clock plant with the help of schematic representation. Mention the phenotype ratio and genotype ratio of plants occurred in F2 generation.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The monohybrid cross in Four o’clock plant is an example of incomplete dominance. It is also called semi-dominance or partial dominance.
Complete Answer:
It was first discovered in Mirabilis and Antirrhinum majus (Snapdragon) by Carl Correns. Incomplete dominance is a phenomenon when neither of the alleles of a gene is fully dominant over the other. The resulting hybrid is an intermediate between the two parents.
Incomplete dominance in Mirabilis Jalapa (Four o’clock plant):
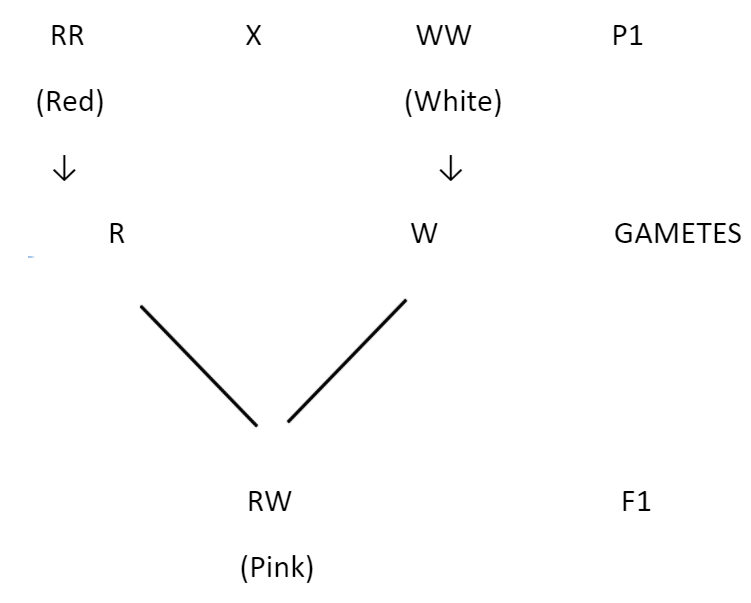
Self pollination of F1 generation plants:
Phenotypic ratio- 1:2:1 (1 red: 2 pink: 1 white)
Genotypic ratio- 1:2:1 (1 RR: 2 Rr: 1rr)
In this, blending of characters has not taken place. The phenotypic and genotypic ratios are the same. The heterozygous Rr represent pink flowers, the dominant homozygous RR shows the red flower and the recessive homozygous rr represents the white flower. Both the genotypic and the phenotypic ratios in the F2 generation are the same i.e. 1:2:1.
Note: Incomplete dominance is a deviation of Mendel’s law of dominance that states that out of two contrasting allelomorphic factors, only one express itself in an individual in F1 generation (dominant) whereas, the other is not expressed (recessive), however the recessive character reappear unchanged in the F2 generation.
Complete Answer:
It was first discovered in Mirabilis and Antirrhinum majus (Snapdragon) by Carl Correns. Incomplete dominance is a phenomenon when neither of the alleles of a gene is fully dominant over the other. The resulting hybrid is an intermediate between the two parents.
Incomplete dominance in Mirabilis Jalapa (Four o’clock plant):

Self pollination of F1 generation plants:
| R | W | |
| R | RRRed | RWPink |
| W | RWPink | WWWhite |
Phenotypic ratio- 1:2:1 (1 red: 2 pink: 1 white)
Genotypic ratio- 1:2:1 (1 RR: 2 Rr: 1rr)
In this, blending of characters has not taken place. The phenotypic and genotypic ratios are the same. The heterozygous Rr represent pink flowers, the dominant homozygous RR shows the red flower and the recessive homozygous rr represents the white flower. Both the genotypic and the phenotypic ratios in the F2 generation are the same i.e. 1:2:1.
Note: Incomplete dominance is a deviation of Mendel’s law of dominance that states that out of two contrasting allelomorphic factors, only one express itself in an individual in F1 generation (dominant) whereas, the other is not expressed (recessive), however the recessive character reappear unchanged in the F2 generation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




