
Explain tautomerism with an example.
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: To solve this we must know that tautomers are isomers of a compound which differ in the position of electrons and protons. The carbon skeleton of the compound remains unchanged. The tautomers exist in equilibrium with each other.
Complete answer:
We know that tautomers are isomers of a compound which differ in the position of electrons and protons. The carbon skeleton of the compound remains unchanged.
-The phenomenon in which a single chemical compound tends to exist in two or more interconvertible structures that differ in terms of the position of one atomic nucleus which is generally a hydrogen is known as tautomerism. The tautomers differ in the number of electrons and protons.
-When reaction occurs between tautomers the transfer of protons occurs.
-In tautomerism, the isomers interchange into or between one another very easily in order to exist together in equilibrium. During the reaction, proton transfer occurs in an intermolecular fashion.
Example of tautomerism is the ketone-enol tautomerism.
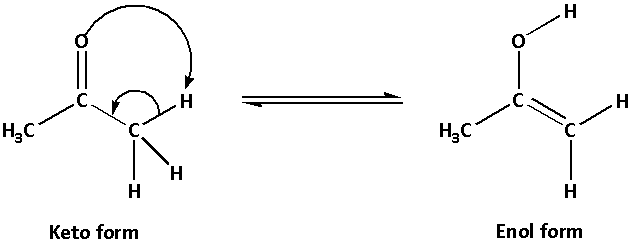
The keto form is more stable than the enol form.
Other examples of tautomerism are: enamine-imine tautomerism, lactam-lactim tautomerism, etc.
The tautomerism process gives the compound more stability. During tautomerism, a hydrogen atom is exchanged between two isomers. Tautomerism is a reversible process.
Note:There are three types of tautomerism:
1-Prototropic tautomerism: Prototropic tautomerism occurs in compounds due to its acid-base behaviour. The tautomers differ in the position of protons.
2-Annular tautomerism: When the proton occupies two or more positions of a heterocyclic system then it is known as annular tautomerism.
3-Valence tautomerism: In valence tautomerism, continuous formation and breaking of single and double bonds occurs without migration of any atoms.
Complete answer:
We know that tautomers are isomers of a compound which differ in the position of electrons and protons. The carbon skeleton of the compound remains unchanged.
-The phenomenon in which a single chemical compound tends to exist in two or more interconvertible structures that differ in terms of the position of one atomic nucleus which is generally a hydrogen is known as tautomerism. The tautomers differ in the number of electrons and protons.
-When reaction occurs between tautomers the transfer of protons occurs.
-In tautomerism, the isomers interchange into or between one another very easily in order to exist together in equilibrium. During the reaction, proton transfer occurs in an intermolecular fashion.
Example of tautomerism is the ketone-enol tautomerism.
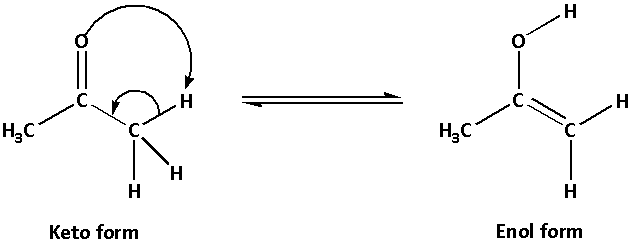
The keto form is more stable than the enol form.
Other examples of tautomerism are: enamine-imine tautomerism, lactam-lactim tautomerism, etc.
The tautomerism process gives the compound more stability. During tautomerism, a hydrogen atom is exchanged between two isomers. Tautomerism is a reversible process.
Note:There are three types of tautomerism:
1-Prototropic tautomerism: Prototropic tautomerism occurs in compounds due to its acid-base behaviour. The tautomers differ in the position of protons.
2-Annular tautomerism: When the proton occupies two or more positions of a heterocyclic system then it is known as annular tautomerism.
3-Valence tautomerism: In valence tautomerism, continuous formation and breaking of single and double bonds occurs without migration of any atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




