
Explain structures of diborane and boric acid.
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: As we know diborane has twelve valence electrons and it is an electron deficient compound. Bridging boron- hydrogen bond has 3c-2e bonds and terminal boron hydrogen bonds in diborane have 2c-2e bonds. Layered structure is present in boric acid.
Complete step by step answer:
(1) Diborane: We know that molecular formula of diborane is ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ . Diborane has six hydrogen atoms and two boron atoms. It is an ethane like structure. From electron diffraction studies we see that diborane has a bridge structure in which two irregular ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ tetrahedral have one edge common. Two boron atoms and four terminal hydrogen atoms are lie in a plane of paper where remaining two hydrogen atoms are located centrally above and below the plane that have two boron atoms and four hydrogen atoms less or more bridging two boron atoms and therefore prevent the rotation between two boron atoms. Now we draw the structure of diborane:
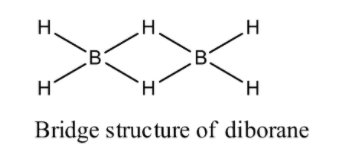
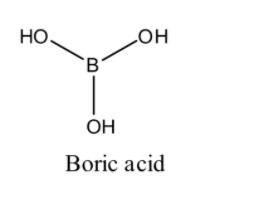
(2) Boric acid: We know that molecular formula of boric acid is ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ . Boric acid is an acid containing one atom of boron, three atoms of hydrogen and three atoms of oxygen. As we know it is a monobasic lewis acid. Now we draw the structure of boric acid:
Note:
We can see from nuclear magnetic resonance study and Raman spectra that four terminal hydrogen atoms are of one type while the remaining two bridging hydrogen atoms are different types in diborane.
Complete step by step answer:
(1) Diborane: We know that molecular formula of diborane is ${{\text{B}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ . Diborane has six hydrogen atoms and two boron atoms. It is an ethane like structure. From electron diffraction studies we see that diborane has a bridge structure in which two irregular ${\text{B}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}$ tetrahedral have one edge common. Two boron atoms and four terminal hydrogen atoms are lie in a plane of paper where remaining two hydrogen atoms are located centrally above and below the plane that have two boron atoms and four hydrogen atoms less or more bridging two boron atoms and therefore prevent the rotation between two boron atoms. Now we draw the structure of diborane:

(2) Boric acid: We know that molecular formula of boric acid is ${{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{B}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ . Boric acid is an acid containing one atom of boron, three atoms of hydrogen and three atoms of oxygen. As we know it is a monobasic lewis acid. Now we draw the structure of boric acid:

Note:
We can see from nuclear magnetic resonance study and Raman spectra that four terminal hydrogen atoms are of one type while the remaining two bridging hydrogen atoms are different types in diborane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




