
Explain saponification of oils/fats with equation.
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: This is the process which is related to the manufacturing of soaps. Soaps are long chained compounds of sodium, and are prepared by using heavy fats and an alkaline medium as reagent.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about soaps. Soaps improve the cleansing properties of water and help in removal of fats which bind other materials to the fabric or skin. Soap chips are made by running a thin sheet of melted soap onto a col cylinder and scraping off the soaps in small broken pieces. Soap granules are dried miniature soap bubbles. Soap powders and souring soaps contain some soup, a scouring reagent(abrasive) such as powdered pumice or finely divided sand and builders like sodium carbonate and trisodium phosphate. Soaps used for cleansing purposes are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids e.g stearic, oleic and palmitic acids. Soaps containing sodium salts are formed by heating fat(i.e glycerol ester of fatty acid) with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. This reaction is known as saponification.
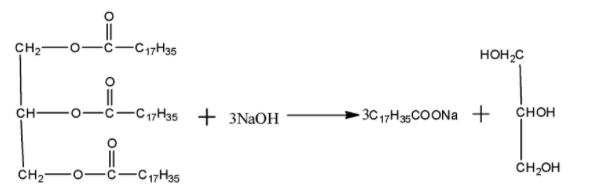
In this reaction, esters of fatty acids are hydrolysed and soap remains in colloidal form. It is precipitated by adding sodium chloride. The solution left after removing soap is recovered by fractional distillation as it contains unwanted compound glycerol. Both sodium and potassium soaps are soluble in water and can be used for cleaning purposes. Generally potassium soaps are softer to the skin than sodium soap. These can be prepared by taking $KOH$ in place of $NaOH$ in the above reaction.
Note: Different types of soaps can be made using different raw materials.
A. Toilet soaps
B. Transparent soaps
C. Medicated soaps
D. Shaving soaps
E. Laundry soaps
Soaps that float in water are made by beating tiny air bubbles before their hardening is done.
Complete answer:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about soaps. Soaps improve the cleansing properties of water and help in removal of fats which bind other materials to the fabric or skin. Soap chips are made by running a thin sheet of melted soap onto a col cylinder and scraping off the soaps in small broken pieces. Soap granules are dried miniature soap bubbles. Soap powders and souring soaps contain some soup, a scouring reagent(abrasive) such as powdered pumice or finely divided sand and builders like sodium carbonate and trisodium phosphate. Soaps used for cleansing purposes are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids e.g stearic, oleic and palmitic acids. Soaps containing sodium salts are formed by heating fat(i.e glycerol ester of fatty acid) with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. This reaction is known as saponification.

In this reaction, esters of fatty acids are hydrolysed and soap remains in colloidal form. It is precipitated by adding sodium chloride. The solution left after removing soap is recovered by fractional distillation as it contains unwanted compound glycerol. Both sodium and potassium soaps are soluble in water and can be used for cleaning purposes. Generally potassium soaps are softer to the skin than sodium soap. These can be prepared by taking $KOH$ in place of $NaOH$ in the above reaction.
Note: Different types of soaps can be made using different raw materials.
A. Toilet soaps
B. Transparent soaps
C. Medicated soaps
D. Shaving soaps
E. Laundry soaps
Soaps that float in water are made by beating tiny air bubbles before their hardening is done.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




