
Explain ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$ reaction with appropriate example.
Answer
557.7k+ views
Hint: ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$ reaction is one of the substitution reactions in organic chemistry. It is a basic reaction which is favoured by polar protic solvents. Polar protic solvents refer to the solvents possessing high value of dipole moment and dielectric constant.
Complete step by step answer:
The $S_{N}$ in the reaction name suggests that it is a nucleophilic substitution and the one suggests that the rate determining step is unimolecular. The process involves a nucleophile that replaces a leaving group. These reactions are unimolecular. In this reaction, the rate only depends on the concentration of one reactant. It is a two-step ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}2$ is faster than ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$. Because ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$ is a single step mechanism.
One example of ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$ reaction is,
${\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_3}{\rm{CBr}} + {}^ - {\rm{OH}} \to {\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COH}} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{r}}^ - }$
We know that ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$reaction takes place in two steps. Let’s understand the mechanism of the above reaction.
In step I, cleavage of ${\rm{C}} - {\rm{Br}}$ bond takes place to produce a carbocation and a bromide ion.
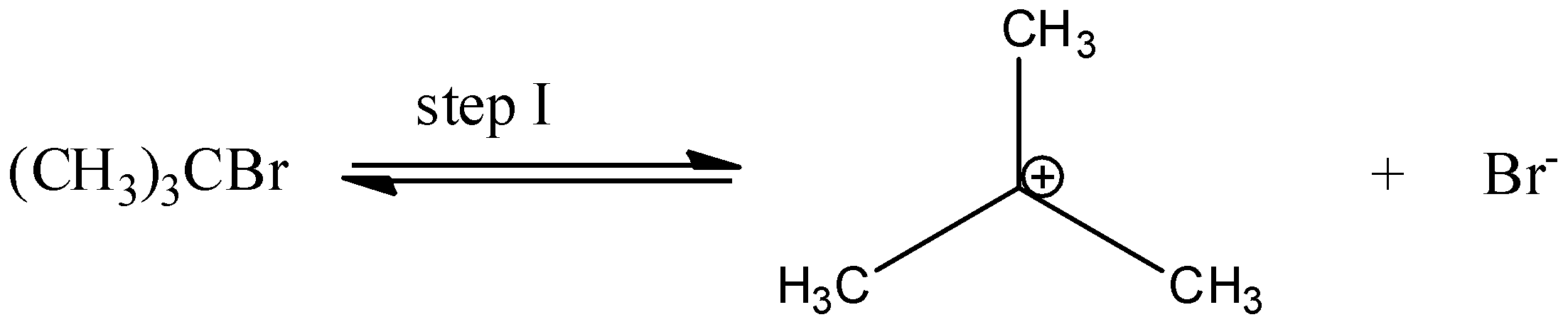
In the 2nd step a nucleophile attacks the carbocation to form alcohol.
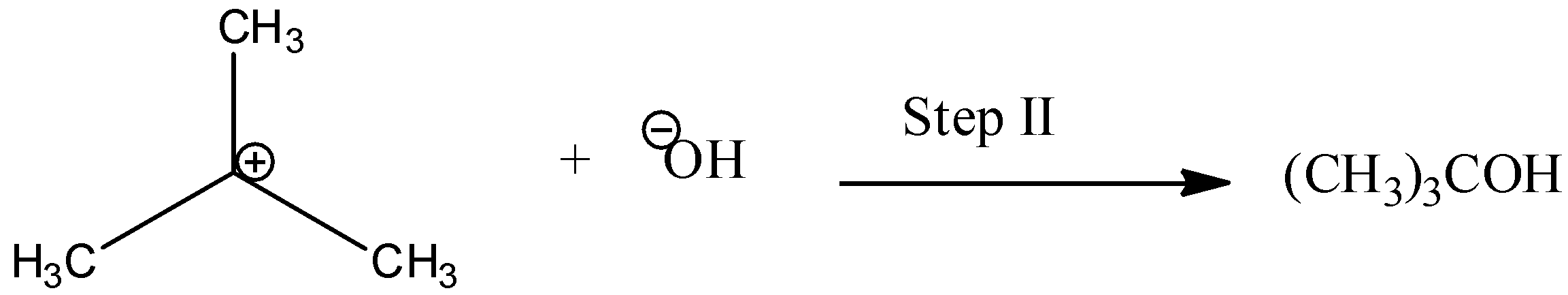
The step I is the reversible and slowest step. It involves the breaking of ${\rm{C}} - {\rm{Br}}$ for which energy is obtained by salvation of the halide ion with the proton of protic solvent. We know that the rate of reaction depends only on the slowest step. So, rate is dependent on concentration on alkyl halide.
Note: Factors that affect rate of $S_{N}1$ reaction:
The rate can also depend on the strength of the incoming nucleophile.
The rate of the reaction can be increased by using highly polar solvent.
$S_{N}1$ reactions generally describe a bond breaking process whereas $S_{N}2$ reactions describe a bond making process. $S_{N}1$ reactions are unimolecular and $S_{N}2$ reactions are bimolecular in rate of the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The $S_{N}$ in the reaction name suggests that it is a nucleophilic substitution and the one suggests that the rate determining step is unimolecular. The process involves a nucleophile that replaces a leaving group. These reactions are unimolecular. In this reaction, the rate only depends on the concentration of one reactant. It is a two-step ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}2$ is faster than ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$. Because ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$ is a single step mechanism.
One example of ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$ reaction is,
${\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_3}{\rm{CBr}} + {}^ - {\rm{OH}} \to {\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COH}} + {\rm{B}}{{\rm{r}}^ - }$
We know that ${{\rm{S}}_{\rm{N}}}1$reaction takes place in two steps. Let’s understand the mechanism of the above reaction.
In step I, cleavage of ${\rm{C}} - {\rm{Br}}$ bond takes place to produce a carbocation and a bromide ion.

In the 2nd step a nucleophile attacks the carbocation to form alcohol.
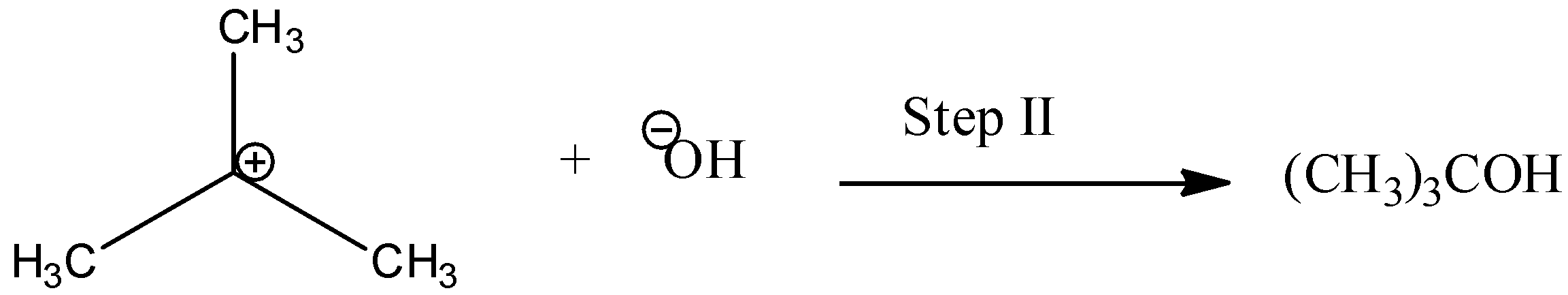
The step I is the reversible and slowest step. It involves the breaking of ${\rm{C}} - {\rm{Br}}$ for which energy is obtained by salvation of the halide ion with the proton of protic solvent. We know that the rate of reaction depends only on the slowest step. So, rate is dependent on concentration on alkyl halide.
Note: Factors that affect rate of $S_{N}1$ reaction:
The rate can also depend on the strength of the incoming nucleophile.
The rate of the reaction can be increased by using highly polar solvent.
$S_{N}1$ reactions generally describe a bond breaking process whereas $S_{N}2$ reactions describe a bond making process. $S_{N}1$ reactions are unimolecular and $S_{N}2$ reactions are bimolecular in rate of the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




