
Explain: Propan-1-ol has a higher boiling point than n-butane.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Propan-1-ol has the functional group of –OH while n-butane has no functional group in it and is a normal alkane. Addition of functional groups leads to changes in certain physical and chemical properties of the compound.
Complete step by step solution:
-There are mainly 4 types of bonds – ionic, covalent, hydrogen and Van der-Waal forces of interaction. Ionic bonds are formed by losing/gaining electrons. Covalent bonds are formed by sharing electrons. Hydrogen bonds are formed by the interaction of lone pairs of electrons with another atom. Van der-Waal forces are physical forces which are dipole-dipole interactions.
-To understand hydrogen bonds, we need to first see what electronegativity is. It is the ability of an atom to attract the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond formation. More is the electron affinity of an atom towards an electron, more is its electronegativity.
-Since the strength of hydrogen bond is governed by the electronegativity of an atom, we can conclude that hydrogen bond will be the strongest in the compounds formed by hydrogen and fluorine atoms. Actually, only three elements can show hydrogen bonding. They are N, O and F.
-Organic compounds are the compounds of carbon, hydrogen and some other elements. They are governed by the ability of carbon to form stable chains or rings with its own atom. This ability is called catenation. It results in huge changes of the characteristics of compounds which are otherwise absent in inorganic compounds.
-Propan-1-ol has a carbon chain of 3 atoms while n-butane has a carbon ring of 4 atoms. In the process of catenation, we generally observe that the melting and boiling points of the compounds increase as we increase the number of carbon atoms present in the chain.
-But here, the condition is reversed. a 3-member chain of propanol has more boiling points than a 4-member chain of butane. This is due to the presence of the functional group on propane which is called hydroxyl.
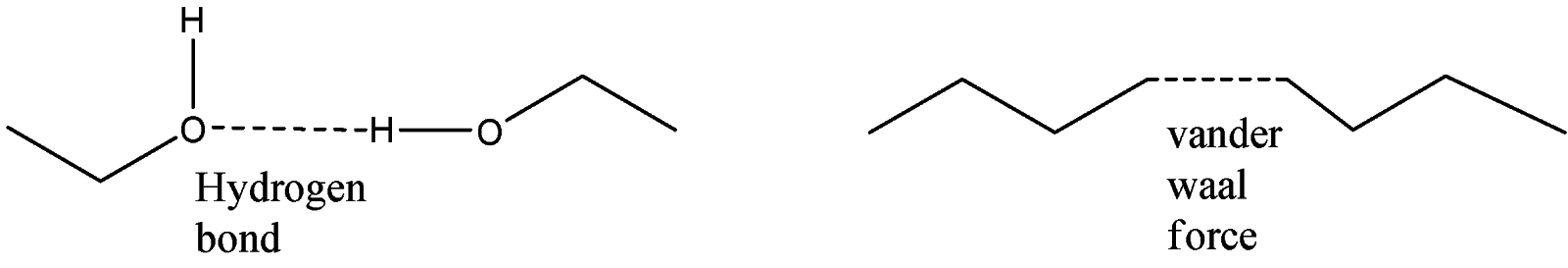
-The –OH group present in Propan-1-ol shows hydrogen bonding which is greater in strength than the Van der Waal force present in n-butane. The bond occurs between the different molecules of the compound. Since the bond is stronger, more heat is required to break the bond and so the boiling point is higher than n-butane.
This can be explained with the help of the structure of Propan-1-ol.
Note: The boiling point of such compounds can be compared only when the difference between the carbon atoms present in the chain is 1, 2 or 3. If more carbon chains are present, then the boiling point will be more for the compound with a larger number of carbon atoms present in it.
Eg, The boiling point of propanol is 97$^{\circ }C$ while that of heptanes is around $98$ $^{\circ }C$ which is more than propanol as it has more carbon atoms in it.
Complete step by step solution:
-There are mainly 4 types of bonds – ionic, covalent, hydrogen and Van der-Waal forces of interaction. Ionic bonds are formed by losing/gaining electrons. Covalent bonds are formed by sharing electrons. Hydrogen bonds are formed by the interaction of lone pairs of electrons with another atom. Van der-Waal forces are physical forces which are dipole-dipole interactions.
-To understand hydrogen bonds, we need to first see what electronegativity is. It is the ability of an atom to attract the shared pair of electrons in a covalent bond formation. More is the electron affinity of an atom towards an electron, more is its electronegativity.
-Since the strength of hydrogen bond is governed by the electronegativity of an atom, we can conclude that hydrogen bond will be the strongest in the compounds formed by hydrogen and fluorine atoms. Actually, only three elements can show hydrogen bonding. They are N, O and F.
-Organic compounds are the compounds of carbon, hydrogen and some other elements. They are governed by the ability of carbon to form stable chains or rings with its own atom. This ability is called catenation. It results in huge changes of the characteristics of compounds which are otherwise absent in inorganic compounds.
-Propan-1-ol has a carbon chain of 3 atoms while n-butane has a carbon ring of 4 atoms. In the process of catenation, we generally observe that the melting and boiling points of the compounds increase as we increase the number of carbon atoms present in the chain.
-But here, the condition is reversed. a 3-member chain of propanol has more boiling points than a 4-member chain of butane. This is due to the presence of the functional group on propane which is called hydroxyl.
-The –OH group present in Propan-1-ol shows hydrogen bonding which is greater in strength than the Van der Waal force present in n-butane. The bond occurs between the different molecules of the compound. Since the bond is stronger, more heat is required to break the bond and so the boiling point is higher than n-butane.
This can be explained with the help of the structure of Propan-1-ol.

Note: The boiling point of such compounds can be compared only when the difference between the carbon atoms present in the chain is 1, 2 or 3. If more carbon chains are present, then the boiling point will be more for the compound with a larger number of carbon atoms present in it.
Eg, The boiling point of propanol is 97$^{\circ }C$ while that of heptanes is around $98$ $^{\circ }C$ which is more than propanol as it has more carbon atoms in it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




