
Explain Mendel’s Monohybrid Cross. Give an example.
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: A cross between two pure homozygous individuals in which only one contrasting trait is taken into account is called monohybrid cross. The monohybrid cross was first carried out by Gregor Mendel to study the inheritance pattern. Due to his research work in genetics, he is known as the father of genetics.
Complete answer:
• In a monohybrid cross, the fertilization takes place between two homozygous parents that differ only in one contrasting character which is being studied. The offspring produced by monohybrid cross are called monohybrids.
• Mendel performed seven types of monohybrid crosses with each cross involving a single character with a contrasting trait.
• Mendel selected garden pea plants for his experiments. The seven characters with contrasting traits studied by Mendel in each cross included were:
- Pea color (Green or Yellow)
- Pea shape (Round or Wrinkled)
- Pod shape (Constricted or Inflated)
- Pod color (Green or Yellow)
- Flower color (Purple or White)
- Flower position (Axial or terminal)
- Plant size (Tall or dwarf)
• In the garden pea plant - pea color, pea shape, pod shape etc are characteristics, while green or yellow, round or wrinkled, constricted or inflated etc are traits.
Example of monohybrid cross:
Mendel initially performed his experiment by taking a pair of garden pea plants with contrasting plant size. One plant was tall and another plant was dwarf. Both the plants were homozygous. The genotype (genetic composition) of a tall plant was TT and that of short plant was tt. Mendel crossed the two plants which produced offspring or progeny known as F1 generation (first filial generation). The progenies produced in F1 generation were hybrid or heterozygous plants (monohybrids) having genotype Tt. However, the monohybrids were of tall phenotype (external appearance).
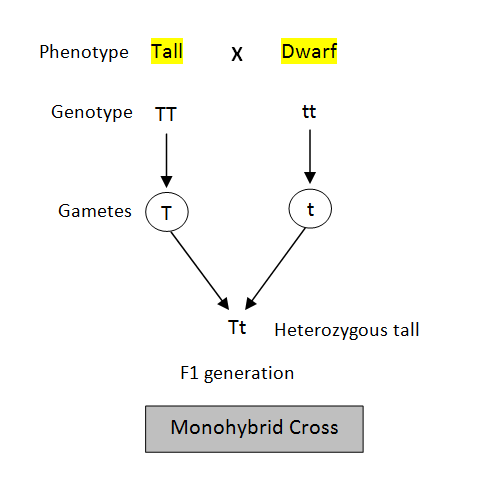
Note: A monohybrid cross involves hybridization between two pure homozygous parents that differ in a single contrasting trait. Monohybrid cross experiments were first done by Mendel using garden pea plants. He observed that the progenies produced in F1 generation after monohybrid cross of two pure homozygous parents are heterozygous.
Complete answer:
• In a monohybrid cross, the fertilization takes place between two homozygous parents that differ only in one contrasting character which is being studied. The offspring produced by monohybrid cross are called monohybrids.
• Mendel performed seven types of monohybrid crosses with each cross involving a single character with a contrasting trait.
• Mendel selected garden pea plants for his experiments. The seven characters with contrasting traits studied by Mendel in each cross included were:
- Pea color (Green or Yellow)
- Pea shape (Round or Wrinkled)
- Pod shape (Constricted or Inflated)
- Pod color (Green or Yellow)
- Flower color (Purple or White)
- Flower position (Axial or terminal)
- Plant size (Tall or dwarf)
• In the garden pea plant - pea color, pea shape, pod shape etc are characteristics, while green or yellow, round or wrinkled, constricted or inflated etc are traits.
Example of monohybrid cross:
Mendel initially performed his experiment by taking a pair of garden pea plants with contrasting plant size. One plant was tall and another plant was dwarf. Both the plants were homozygous. The genotype (genetic composition) of a tall plant was TT and that of short plant was tt. Mendel crossed the two plants which produced offspring or progeny known as F1 generation (first filial generation). The progenies produced in F1 generation were hybrid or heterozygous plants (monohybrids) having genotype Tt. However, the monohybrids were of tall phenotype (external appearance).

Note: A monohybrid cross involves hybridization between two pure homozygous parents that differ in a single contrasting trait. Monohybrid cross experiments were first done by Mendel using garden pea plants. He observed that the progenies produced in F1 generation after monohybrid cross of two pure homozygous parents are heterozygous.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




