
Explain Kolbe’s reaction with one example.
Answer
527.2k+ views
Hint: The reaction given in the question is one of the most important named reactions in organic chemistry. It is widely used in the synthesis of salicylic acid and its derivatives.
Complete step by step answer:
Kolbe’s reaction, also known as Kolbe-Schmitt reaction is a very important reaction in organic chemistry. It is a reaction for the synthesis of salicylic acid and its derivatives by carboxylation of phenols in a basic solution.
The Reaction for Kolbe’s reaction is given below –
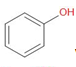 \[\xrightarrow[NaOH]{C{{O}_{2}}}\]
\[\xrightarrow[NaOH]{C{{O}_{2}}}\]
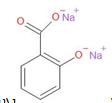 \[\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}\]
\[\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}\]
The detailed mechanism of this reaction is as follows –
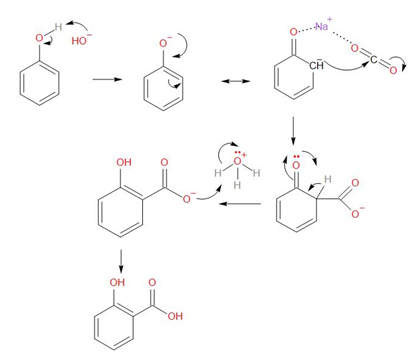
As we can see, the given reaction is an example of Nucleophilic addition, where there is a Nucleophilic addition of sodium phenoxide to carbon dioxide gas to form the sodium salicylate in the mechanism. This reaction takes place under these conditions –
• Temperature = 400K
• Pressure = 4 - 7 atm.
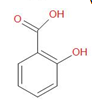
Sodium salicylate on further reaction in an acidic medium gives salicylic acid.
Additional information: Sodium salicylate is not the only product in the reaction, it is the major product. The by-products produced are very small in quantity, so we don’t take it into account.
Note: To define Kolbe’s reaction, you can write, “When phenol is treated with sodium hydroxide, sodium phenoxide is produced. This sodium phenoxide when treated with carbon dioxide, followed by acidification, undergoes electrophilic substitution to give ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid as the main product. This reaction is known as Kolbe's reaction”.
Complete step by step answer:
Kolbe’s reaction, also known as Kolbe-Schmitt reaction is a very important reaction in organic chemistry. It is a reaction for the synthesis of salicylic acid and its derivatives by carboxylation of phenols in a basic solution.
The Reaction for Kolbe’s reaction is given below –



The detailed mechanism of this reaction is as follows –

As we can see, the given reaction is an example of Nucleophilic addition, where there is a Nucleophilic addition of sodium phenoxide to carbon dioxide gas to form the sodium salicylate in the mechanism. This reaction takes place under these conditions –
• Temperature = 400K
• Pressure = 4 - 7 atm.
Sodium salicylate on further reaction in an acidic medium gives salicylic acid.
Additional information: Sodium salicylate is not the only product in the reaction, it is the major product. The by-products produced are very small in quantity, so we don’t take it into account.
Note: To define Kolbe’s reaction, you can write, “When phenol is treated with sodium hydroxide, sodium phenoxide is produced. This sodium phenoxide when treated with carbon dioxide, followed by acidification, undergoes electrophilic substitution to give ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid as the main product. This reaction is known as Kolbe's reaction”.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




