
Explain how do you prioritize the different groups on chiral centers?
Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint:Chiral center or chiral atom is a tetrahedral atom which has four different groups attached with it. Compounds with chiral carbon atom are termed as chiral compounds. These compounds have many isomers, and these isomers can be represented by different configurations. One such configuration is R and S type of configuration which involves prioritizing the groups based on certain rules.
Complete step-by-step answer: The different Stereoisomers of a molecule can be expressed in terms of R and S configuration. This method was proposed by Cahn, Ingold and Prelog. This method has been accepted by IUPAC. it is based on the assignment of priorities to the atoms or groups attached to the central carbon atom.
The priorities can be assigned on the basis of following rules.
Rule 1: If four atoms attached to the chiral carbon atom are all different, then priority depends upon atomic number. This means that atom having the higher atomic number gets the higher priority than the atom having the lower atomic number.
For example: Consider the given compound:
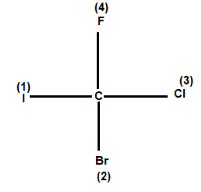
In the above compound four different atom (different halogen atoms) are attached at the carbon. Now we know that Iodine has the highest atomic number, followed by bromine chlorine and the least is of fluorine. So, as per the Rule-1, iodine gets first priority followed by Br, Cl, F. the number (1) (2) (3) (4) shows the priority order.
Rule 2: If the relative priority of the two groups cannot be decided by the rule 1 (on the basis of atomic number of the atoms that are directly attached with the carbon), then we consider the next atoms for the assignment of priority.
For example: Consider the given compound:
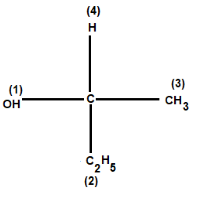
For instance, if $C{{H}_{3}}\And {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$are attached as in the above case, then ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$gets higher priority as the atoms attached to the first carbon atom are C, H and H whereas in $C{{H}_{3}}$group, atoms attached are only H, H and H. This is because in ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$first carbon atom is attached to a carbon atom also, and in $C{{H}_{3}}$group we can see that only hydrogens are attached and we know we know that atomic number of C > H.
Therefore, in the above compound OH gets the first priority as oxygen has highest atomic number among C, H O. and then ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$gets second priority followed by $C{{H}_{3}}$and hydrogen with least atomic number gets fourth priority.
Note:It should be noted that one should know how to name the configurations that is whether a compound is R or S. For this,
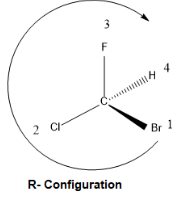
we start from the lowest priority group and move toward the highest priority group. While moving if the movement is clockwise then the configuration is R and if it is anticlockwise then the configuration becomes S. the same is depicted below.
Complete step-by-step answer: The different Stereoisomers of a molecule can be expressed in terms of R and S configuration. This method was proposed by Cahn, Ingold and Prelog. This method has been accepted by IUPAC. it is based on the assignment of priorities to the atoms or groups attached to the central carbon atom.
The priorities can be assigned on the basis of following rules.
Rule 1: If four atoms attached to the chiral carbon atom are all different, then priority depends upon atomic number. This means that atom having the higher atomic number gets the higher priority than the atom having the lower atomic number.
For example: Consider the given compound:

In the above compound four different atom (different halogen atoms) are attached at the carbon. Now we know that Iodine has the highest atomic number, followed by bromine chlorine and the least is of fluorine. So, as per the Rule-1, iodine gets first priority followed by Br, Cl, F. the number (1) (2) (3) (4) shows the priority order.
Rule 2: If the relative priority of the two groups cannot be decided by the rule 1 (on the basis of atomic number of the atoms that are directly attached with the carbon), then we consider the next atoms for the assignment of priority.
For example: Consider the given compound:

For instance, if $C{{H}_{3}}\And {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$are attached as in the above case, then ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$gets higher priority as the atoms attached to the first carbon atom are C, H and H whereas in $C{{H}_{3}}$group, atoms attached are only H, H and H. This is because in ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$first carbon atom is attached to a carbon atom also, and in $C{{H}_{3}}$group we can see that only hydrogens are attached and we know we know that atomic number of C > H.
Therefore, in the above compound OH gets the first priority as oxygen has highest atomic number among C, H O. and then ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$gets second priority followed by $C{{H}_{3}}$and hydrogen with least atomic number gets fourth priority.
Note:It should be noted that one should know how to name the configurations that is whether a compound is R or S. For this,
we start from the lowest priority group and move toward the highest priority group. While moving if the movement is clockwise then the configuration is R and if it is anticlockwise then the configuration becomes S. the same is depicted below.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




