
Explain ETS and oxidative phosphorylation.
Answer
530.4k+ views
Hint: Electron transport system is made up of membrane proteins. It involves redox-reactions, i.e. electrons are transferred from one molecule to another.
Step by step answer: The process of oxidative phosphorylation involves a flow of electrons through the electron transport chain, which is basically a series of proteins and electron carriers present within the mitochondrial membrane. This flow of electrons allows the electron transport chain to pump protons to at least one side of the mitochondrial membrane. There are several cellular processes which cause the oxidation (“burning”) of varied cellular food sources (like glycolysis, Krebs’s cycle) and the oxidation of amino acids. The electron transport chain builds up an outsized number of hydrogen ions within the intermembrane space. It does so by using up the energy it receives from the passing electrons through a series of energy-releasing reactions. The ultimate step of oxidative phosphorylation is the generation of ATP or the method of phosphorylation. This process takes place with the help of a complex called ATP synthase. In this process, ATP is made as a result of the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH 2 to O 2 by a series of electron carriers or transporters. This process, which takes place in mitochondria, is the major source of ATP in aerobic organisms.
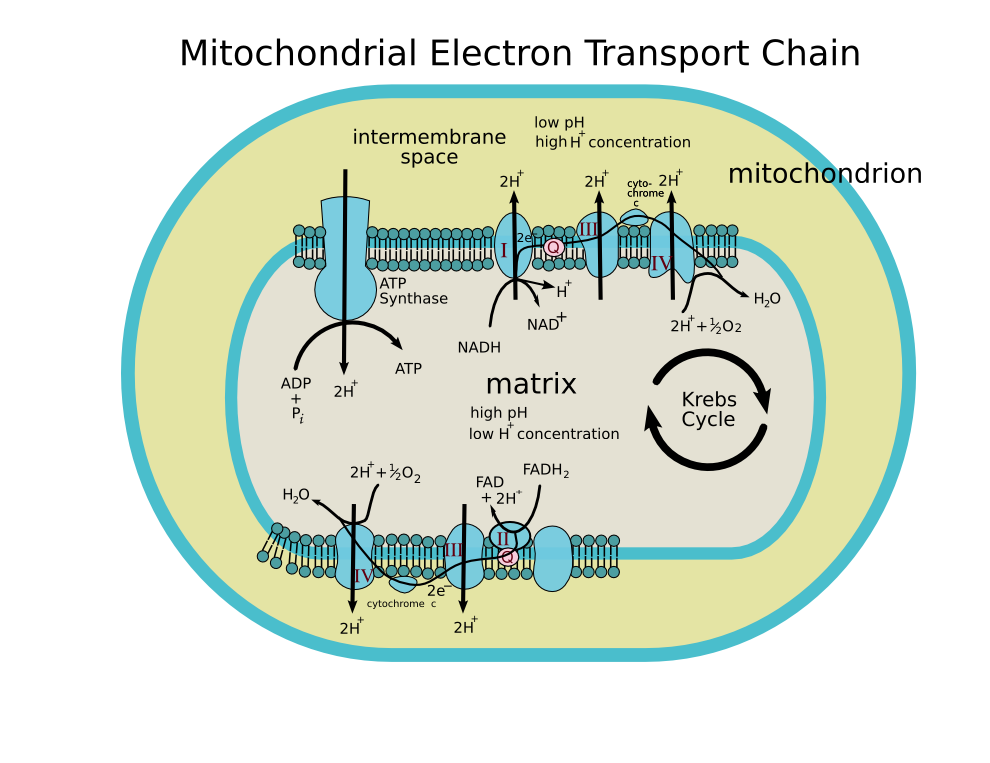
Note: It is important to note that oxidative phosphorylation is formed from two closely connected components: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. Within the electron transport chain, electrons are passed from one molecule to another, and energy released in these electron transfers is taken into use to make an electrochemical gradient, followed by a chemiosmotic activity.
Step by step answer: The process of oxidative phosphorylation involves a flow of electrons through the electron transport chain, which is basically a series of proteins and electron carriers present within the mitochondrial membrane. This flow of electrons allows the electron transport chain to pump protons to at least one side of the mitochondrial membrane. There are several cellular processes which cause the oxidation (“burning”) of varied cellular food sources (like glycolysis, Krebs’s cycle) and the oxidation of amino acids. The electron transport chain builds up an outsized number of hydrogen ions within the intermembrane space. It does so by using up the energy it receives from the passing electrons through a series of energy-releasing reactions. The ultimate step of oxidative phosphorylation is the generation of ATP or the method of phosphorylation. This process takes place with the help of a complex called ATP synthase. In this process, ATP is made as a result of the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH 2 to O 2 by a series of electron carriers or transporters. This process, which takes place in mitochondria, is the major source of ATP in aerobic organisms.

Note: It is important to note that oxidative phosphorylation is formed from two closely connected components: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis. Within the electron transport chain, electrons are passed from one molecule to another, and energy released in these electron transfers is taken into use to make an electrochemical gradient, followed by a chemiosmotic activity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




