
Explain band theory?
Answer
503.1k+ views
Hint: The electronic band structure (or simply band structure) of a material in solid-state physics explains the range of energy levels that electrons can have within it, as well as the ranges of energy levels that they can't have (called band gaps or forbidden bands).
Complete answer:
Solids have a different band theory than liquids and gases because the atoms are packed so close together that the energy levels of the outermost orbital electrons are influenced. The energy level of the innermost electrons, on the other hand, is unaffected by the nearby atoms.
There are many energy bands in the band theory of solids, but the three most important energy bands in solids are:
1.Valence band
2.Conduction band
3.Forbidden band
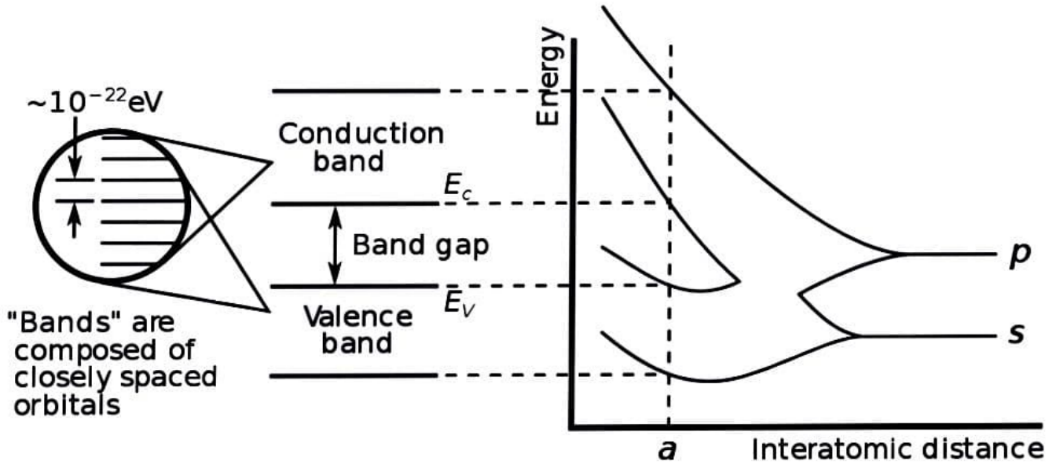
Valence band :The valence band is an energy band made up of valence electron energy levels. The valence band is located beneath the conduction band, and its electrons are freely connected to the atom's nucleus.
Conduction band: The conduction band is the energy band that comprises free electron energy levels. External energy must be applied in order for the valence electrons to be pushed into the conduction band and become free.
Forbidden band :The forbidden band, also known as the forbidden gap, is the energy gap that exists between the valence band and the conduction band. The forbidden gap, as well as the classification of materials as conductors, semiconductors, and insulators, define the electrical conductivity of a solid.
Note:
As atoms get closer to one another and finally form a solid, they generate an energy continuum, which we refer to as bands. The energy levels accessible inside the bands are constant. As a result, it's no surprise that this theory's name is "The Band Theory of Solids."
Complete answer:
Solids have a different band theory than liquids and gases because the atoms are packed so close together that the energy levels of the outermost orbital electrons are influenced. The energy level of the innermost electrons, on the other hand, is unaffected by the nearby atoms.
There are many energy bands in the band theory of solids, but the three most important energy bands in solids are:
1.Valence band
2.Conduction band
3.Forbidden band

Valence band :The valence band is an energy band made up of valence electron energy levels. The valence band is located beneath the conduction band, and its electrons are freely connected to the atom's nucleus.
Conduction band: The conduction band is the energy band that comprises free electron energy levels. External energy must be applied in order for the valence electrons to be pushed into the conduction band and become free.
Forbidden band :The forbidden band, also known as the forbidden gap, is the energy gap that exists between the valence band and the conduction band. The forbidden gap, as well as the classification of materials as conductors, semiconductors, and insulators, define the electrical conductivity of a solid.
Note:
As atoms get closer to one another and finally form a solid, they generate an energy continuum, which we refer to as bands. The energy levels accessible inside the bands are constant. As a result, it's no surprise that this theory's name is "The Band Theory of Solids."
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




