
Explain Adsorption theory of Heterogeneous Catalysis.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint:Adsorption is a Surface phenomenon, i.e. the molecules of the adsorbate do not enter inside the adsorbent, they just stick to the surface. Hence, to solve this problem, firstly we should understand about surface chemistry, Adsorption, Catalyst, then we will learn about the Adsorption theory of Heterogeneous catalysis.
Complete step by step solution:
> Adsorption: The incident of attracting and retaining the substance by a solid (or a liquid) on its surface resulting in a higher concentration of molecules on the surface is known as Adsorption.
Ex: Clay, Silica
> Catalyst: It is defined as a substance that can be added to a reaction to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the process.
> Absorption theory of heterogeneous catalysis, when the reactants of gaseous state or in dissolved state in any solution they adhere on the surface of a suitable catalyst in the solid state. As a result, the concentration of the reactant of the surface of the catalyst availability and probability of the phenomena of a reaction between two increases, and thus the rate of the reaction increases. Also, during the adsorption of reactants to the surface of the catalyst, some amount of energy is released as the process is exothermic in nature.
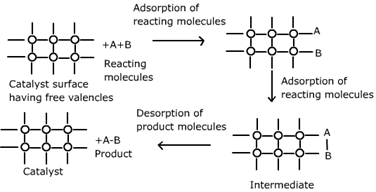
Note: Adsorption hypothesis of catalysis based on the mechanism of heterogeneous catalysis. According to the perspective when the catalyst is in solid phase and the reactants are in gaseous phase or in solution, the molecules of the reactants get absorbed on the catalyst surface. Adsorption is an exothermic process, the heat of adsorption is held by the catalyst surface, which is used on enhancing the chemical movement of reactants molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
> Adsorption: The incident of attracting and retaining the substance by a solid (or a liquid) on its surface resulting in a higher concentration of molecules on the surface is known as Adsorption.
Ex: Clay, Silica
> Catalyst: It is defined as a substance that can be added to a reaction to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the process.
> Absorption theory of heterogeneous catalysis, when the reactants of gaseous state or in dissolved state in any solution they adhere on the surface of a suitable catalyst in the solid state. As a result, the concentration of the reactant of the surface of the catalyst availability and probability of the phenomena of a reaction between two increases, and thus the rate of the reaction increases. Also, during the adsorption of reactants to the surface of the catalyst, some amount of energy is released as the process is exothermic in nature.

Note: Adsorption hypothesis of catalysis based on the mechanism of heterogeneous catalysis. According to the perspective when the catalyst is in solid phase and the reactants are in gaseous phase or in solution, the molecules of the reactants get absorbed on the catalyst surface. Adsorption is an exothermic process, the heat of adsorption is held by the catalyst surface, which is used on enhancing the chemical movement of reactants molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




