
Expand ATP
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint:It consists of a nitrogen base that has double rings. The nitrogen base has an amine group on carbon 6 and additional double bond too which is absent in other types of purine.
Complete answer:
ATP is the energy currency of the cell. It is a nucleotide coenzyme. It is a form of chemical energy of the cell.
Nucleotide = Nucleoside + Phosphate (Nucleoside = Nitrogen base + Sugar)
Hence,
Nucleotide = Nitrogen base + Sugar + Phosphate
Purines are Adenine and Guanine while Pyrimidines are Cytosine and Thymine (Uracil is nitrogen base in RNA only)
Hence,
Adenine + Pentose sugar + Phosphate = Adenylic acid / Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
Thus AMP combines with two phosphate bonds to form ATP and this is the main energy currency of the cell.
ATP stands for Adenosine triphosphate. Adenosine triphosphate is a nucleotide. Its chemical formula is $C_10H_16N_5O_13P_3$
Energy is released when phosphate bonds are broken.
The reaction is as follows :
ATP ⇄ ADP + iP
Thus ATP breaks to form ADP and thus energy is released and ADP absorbs energy to form ATP.
Phosphate bonds in ATP
In ATP, the three phosphate groups are attached to the nucleoside Adenosine.
The three phosphates are termed as alpha, beta and gamma.
Alpha is directly attached to the ribose sugar.
The bond is a phosphodiester bond.
The three phosphate groups are attached by unstable phosphoric acid anhydride bonds.
Magnesium ion is attached to the beta and gamma bonds.
Magnesium acts as coenzyme.
Structure
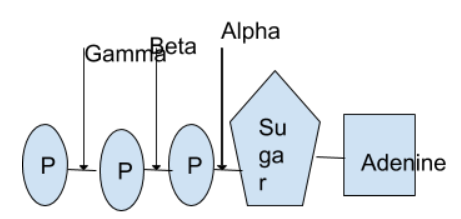
Note:ATP, GTP, UTP< CTP aare energy compounds as these take place in metabolic reactions. However the main energy currency is the ATP because it can break the phosphate bonds easily and thus release of energy takes place easily to carry out metabolic reactions.
Complete answer:
ATP is the energy currency of the cell. It is a nucleotide coenzyme. It is a form of chemical energy of the cell.
Nucleotide = Nucleoside + Phosphate (Nucleoside = Nitrogen base + Sugar)
Hence,
Nucleotide = Nitrogen base + Sugar + Phosphate
Purines are Adenine and Guanine while Pyrimidines are Cytosine and Thymine (Uracil is nitrogen base in RNA only)
Hence,
Adenine + Pentose sugar + Phosphate = Adenylic acid / Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
Thus AMP combines with two phosphate bonds to form ATP and this is the main energy currency of the cell.
ATP stands for Adenosine triphosphate. Adenosine triphosphate is a nucleotide. Its chemical formula is $C_10H_16N_5O_13P_3$
Energy is released when phosphate bonds are broken.
The reaction is as follows :
ATP ⇄ ADP + iP
Thus ATP breaks to form ADP and thus energy is released and ADP absorbs energy to form ATP.
Phosphate bonds in ATP
In ATP, the three phosphate groups are attached to the nucleoside Adenosine.
The three phosphates are termed as alpha, beta and gamma.
Alpha is directly attached to the ribose sugar.
The bond is a phosphodiester bond.
The three phosphate groups are attached by unstable phosphoric acid anhydride bonds.
Magnesium ion is attached to the beta and gamma bonds.
Magnesium acts as coenzyme.
Structure

Note:ATP, GTP, UTP< CTP aare energy compounds as these take place in metabolic reactions. However the main energy currency is the ATP because it can break the phosphate bonds easily and thus release of energy takes place easily to carry out metabolic reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




