
What is an example of a Neutral Mutation?
Answer
489.3k+ views
Hint: Mutation was first introduced by Hugo de Vries. This term was used by him for large spontaneous inheritable changes which occur suddenly in a naturally reproducing population. Based on mutation theory there are two types of mutations- Somatic and Germinal mutation. Somatic mutation occurs in somatic cells and germinal mutation takes place in gametes.
Complete answer-
Mutation based on genes and chromosomes are categorized into the involvement of depending on the number of gene loci. Neutral mutation is the DNA sequence which undergoes changes that are neither beneficial nor harmful to the organism. The genes which undergo neutral mutation do not see much changes in the survival and reproduction.
In genetics the neutral mutations do not affect much the species of are termed as natural selections. It is the linkage between other alleles which are under selection may proceed to loss via genetic hitchhiking and background selection.
When many mutations in a genome decrease an organism’s ability where mutations are not selected for future generations. The variation within the among species is neutral and on the basis of molecular clocks to identify events as speciation and adaptive radiations.
The evolutionary theory is the part of neutral mutation in the . This theory suggests that neutrals are responsible for a large portion of DNA and species. Example- bovine and human insulin in amino acid sequence.
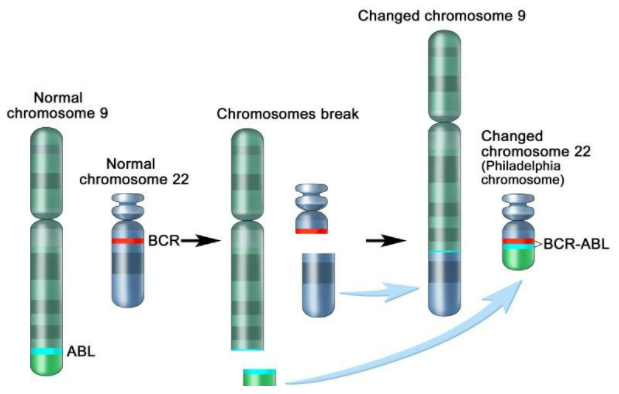
Note:
The function of mutations is to bring undesirable changes and sudden changes in the organism. The mutation part is controlled by genes. Some mutations can be beneficial which occur in bacteria for the survival of antibiotic drugs which leads to development of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria. On the survival basis mutations have advantages and disadvantages too.
Complete answer-
Mutation based on genes and chromosomes are categorized into the involvement of depending on the number of gene loci. Neutral mutation is the DNA sequence which undergoes changes that are neither beneficial nor harmful to the organism. The genes which undergo neutral mutation do not see much changes in the survival and reproduction.
In genetics the neutral mutations do not affect much the species of are termed as natural selections. It is the linkage between other alleles which are under selection may proceed to loss via genetic hitchhiking and background selection.
When many mutations in a genome decrease an organism’s ability where mutations are not selected for future generations. The variation within the among species is neutral and on the basis of molecular clocks to identify events as speciation and adaptive radiations.
The evolutionary theory is the part of neutral mutation in the . This theory suggests that neutrals are responsible for a large portion of DNA and species. Example- bovine and human insulin in amino acid sequence.

Note:
The function of mutations is to bring undesirable changes and sudden changes in the organism. The mutation part is controlled by genes. Some mutations can be beneficial which occur in bacteria for the survival of antibiotic drugs which leads to development of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria. On the survival basis mutations have advantages and disadvantages too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




