
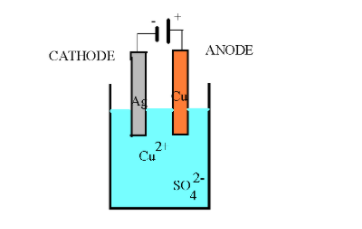
Examine the drawing of an electrolytic cell below: Determine the mass of silver that could be plated if 0.452 A of current is applied for 1.5 hours.

Answer
567k+ views
Hint: The concept of Faraday’s Law of electrolysis is to be used in this question. According to the law, more the current or more the time used in electrolysis, more is the mass of substance deposited at the cathode.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about the Faraday's Law of electrolysis. The passage of electricity through the electrolytes in their dissolved or molten state can cause chemical changes under some conditions. For example, the passing electricity through the acidified water can result in the formation of oxygen and hydrogen gases. The process of chemical decomposition of the electrolyte by the passing electricity through its dissolved or molten state is called electrolysis.
The relationship between the quantity of electricity passed and the quantity of a substance liberated at the electrode is given in the form of Faraday's laws of electrolysis. Faraday's First Law of Electrolysis. This law states that the mass of a substance liberated at the electrode is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte. Mathematically,
\[Q=nF\,and\,m=\dfrac{EIT}{F}\]
Where m is mass deposited, I is current, T is time and F is faraday's constant. E is the equivalent weight which is the ratio of molecular weight and n-factor. As the n-factor is 1, so we get
\[w=\dfrac{108\times 0.452\times 1.5\times 60\times 60}{96500}=2.73g\]
Hence, 2.73 grams of mass of silver is deposited.
NOTE: Electrochemical equivalent of a substance is the amount of substance liberated at the electrode when current of one ampere is passed through the electrolyte for one second.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to answer our question, we need to know about the Faraday's Law of electrolysis. The passage of electricity through the electrolytes in their dissolved or molten state can cause chemical changes under some conditions. For example, the passing electricity through the acidified water can result in the formation of oxygen and hydrogen gases. The process of chemical decomposition of the electrolyte by the passing electricity through its dissolved or molten state is called electrolysis.
The relationship between the quantity of electricity passed and the quantity of a substance liberated at the electrode is given in the form of Faraday's laws of electrolysis. Faraday's First Law of Electrolysis. This law states that the mass of a substance liberated at the electrode is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte. Mathematically,
\[Q=nF\,and\,m=\dfrac{EIT}{F}\]
Where m is mass deposited, I is current, T is time and F is faraday's constant. E is the equivalent weight which is the ratio of molecular weight and n-factor. As the n-factor is 1, so we get
\[w=\dfrac{108\times 0.452\times 1.5\times 60\times 60}{96500}=2.73g\]
Hence, 2.73 grams of mass of silver is deposited.
NOTE: Electrochemical equivalent of a substance is the amount of substance liberated at the electrode when current of one ampere is passed through the electrolyte for one second.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




