
Evaluate the magnitude and direction of magnetic field at point O:
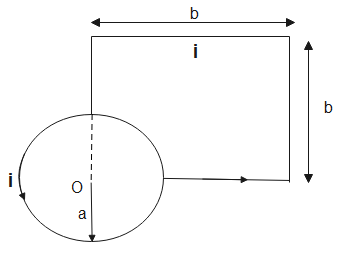
(A). $\dfrac{3{{\mu }_{0}}i}{8a},\,\odot $
(B). $\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}b},\,\odot $
(C). $\dfrac{3{{\mu }_{0}}i}{8a}+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}b},\,\odot $
(D). $\dfrac{3{{\mu }_{0}}i}{8a}+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}b},\,\otimes $

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: The magnetic field due to different elements is different. We can use the gauss law of magnetism to calculate magnetic fields due to different elements. The magnetic field at the axis of elements is zero. The right hand thumb rule is used to determine the direction of magnetic field due to a current carrying wire.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given figure,
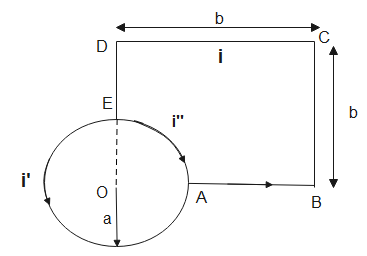
The current will divide at junction E, the current will divide according to the ratio in which the wire is divided between the junctions.
The magnetic field at point O will be the sum of all magnetic fields due to different elements of the wire.
Magnetic field at the centre of a circular wire is given by-
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2r}$
Here,$B$ is the magnetic field
${{\mu }_{0}}$ is the permittivity of free space
$I$ is the flowing through the circular wire
$r$ is the radius of the circle
Therefore, b y the above equation, the magnetic field at point O due to the circular wire is-
${{B}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i'}{2r}$
$\therefore {{B}_{1}}=\dfrac{3{{\mu }_{0}}i}{8r}$ --------- (1)
A current carrying wire gives rise to a magnetic field, which is given as,
$B'=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi r}(\sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}})$
Here, ${{\theta }_{1}}$ is the angle subtended by the upper part of wire at point O
${{\theta }_{2}}$ is the angle subtended by the lower part of the wire at point O.
Magnetic fields due to elements DE and AB are zero as the point O is along the axis.
Magnetic field due to BC and CD is-
$\begin{align}
& {{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi b}(\sin {{45}^{0}}+\sin 0)+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi b}(\sin {{45}^{0}}+\sin 0) \\
& \Rightarrow {{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\sqrt{2}\pi b}+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\sqrt{2}\pi b} \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore {{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi b}$ ----------- (2)
The magnetic field due to elements BC and CD are in the same direction by right hand thumb rule, therefore they are added.
From eq (1) and eq (2), the magnetic fields due to all the elements are in the same direction, I.e. out of the plane of the paper, towards the observer, therefore, the total magnetic field acting on point O is-
$\begin{align}
& B'={{B}_{1}}+{{B}_{2}}\odot \\
& \therefore B'=\dfrac{3{{\mu }_{0}}i}{8r}+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi b}\odot \\
\end{align}$
The magnetic field at point O is $B'=\dfrac{3{{\mu }_{0}}i}{8r}+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi b}\odot $.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Magnetic field describes the influence of magnets and magnetic materials on their surroundings, especially charged particles. The magnetic field can also be described by the total magnetic flux originating from a Gaussian surface. According to the right hand thumb rule, if the thumb is in the direction of current, then the fingers are in the direction of the magnetic field.
Complete step by step solution:

In the given figure,

The current will divide at junction E, the current will divide according to the ratio in which the wire is divided between the junctions.
The magnetic field at point O will be the sum of all magnetic fields due to different elements of the wire.
Magnetic field at the centre of a circular wire is given by-
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2r}$
Here,$B$ is the magnetic field
${{\mu }_{0}}$ is the permittivity of free space
$I$ is the flowing through the circular wire
$r$ is the radius of the circle
Therefore, b y the above equation, the magnetic field at point O due to the circular wire is-
${{B}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i'}{2r}$
$\therefore {{B}_{1}}=\dfrac{3{{\mu }_{0}}i}{8r}$ --------- (1)
A current carrying wire gives rise to a magnetic field, which is given as,
$B'=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi r}(\sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}})$
Here, ${{\theta }_{1}}$ is the angle subtended by the upper part of wire at point O
${{\theta }_{2}}$ is the angle subtended by the lower part of the wire at point O.
Magnetic fields due to elements DE and AB are zero as the point O is along the axis.
Magnetic field due to BC and CD is-
$\begin{align}
& {{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi b}(\sin {{45}^{0}}+\sin 0)+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi b}(\sin {{45}^{0}}+\sin 0) \\
& \Rightarrow {{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\sqrt{2}\pi b}+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\sqrt{2}\pi b} \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore {{B}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi b}$ ----------- (2)
The magnetic field due to elements BC and CD are in the same direction by right hand thumb rule, therefore they are added.
From eq (1) and eq (2), the magnetic fields due to all the elements are in the same direction, I.e. out of the plane of the paper, towards the observer, therefore, the total magnetic field acting on point O is-
$\begin{align}
& B'={{B}_{1}}+{{B}_{2}}\odot \\
& \therefore B'=\dfrac{3{{\mu }_{0}}i}{8r}+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi b}\odot \\
\end{align}$
The magnetic field at point O is $B'=\dfrac{3{{\mu }_{0}}i}{8r}+\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi b}\odot $.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Magnetic field describes the influence of magnets and magnetic materials on their surroundings, especially charged particles. The magnetic field can also be described by the total magnetic flux originating from a Gaussian surface. According to the right hand thumb rule, if the thumb is in the direction of current, then the fingers are in the direction of the magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




