
How do you evaluate $\sin \left( \dfrac{11\pi }{2} \right)$ ?
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: Try to expand $\sin \left( \dfrac{11\pi }{2} \right)$ and express it in the values that we already know the sin and cos of as, $\dfrac{11\pi }{2}=5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ . Then use the trigonometric identity $\sin (a+b)=\sin a\cos b+\sin b\cos a$ to express $\sin \left( \dfrac{11\pi }{2} \right)$ as $\sin \left( 5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ . Here, a is $5\pi $ and b is $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ .
Complete step by step answer:
This type of question is mainly asked to check whether one remembers the formula $\sin (a+b)=\sin a\cos b+\sin b\cos a$ and the values of sin and cos at $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and $n\pi $ .
We know, $\sin (n\pi )$ is 0 for all n belonging to integers, $\sin \left( \dfrac{(4n+1)\pi }{2} \right)$ is 1 for all n belonging to integers, $\cos \left( \dfrac{\left( 2n+1 \right)\pi }{2} \right)$ is 0 for all n belonging to integers and $\cos \left( \left( 2n+1 \right)\pi \right)$ is -1 for all n belonging to integers.
We know, $\dfrac{11\pi }{2}=\dfrac{10\pi +\pi }{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{11\pi }{2}=\dfrac{10\pi }{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Since 10 is divisible by 2 and when dividing 10 by 2 we get 5,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{10\pi }{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{2}=5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Thus, $\sin \left( \dfrac{11\pi }{2} \right)=\sin \left( 5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$
Now, taking a as $5\pi $ and b as $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and applying it in the formula of $\sin (a+b)=\sin a\cos b+\sin b\cos a$ we have,
$\sin \left( 5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\sin \left( 5\pi \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)+\cos \left( 5\pi \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ .
$\sin \left( 5\pi \right)$ is of the form $\sin \left( n\pi \right)$ so equal to 0 , $\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ is of the form $\sin \left( \dfrac{(4n+1)\pi }{2} \right)$ so equal to 1 , $\cos \left( 5\pi \right)$ is of the form $\cos \left( \left( 2n+1 \right)\pi \right)$ so equal to -1 and $\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ is of the form $\cos \left( \dfrac{\left( 2n+1 \right)\pi }{2} \right)$ so equal to 0.
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( 5\pi \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)+\cos \left( 5\pi \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=0\times 0+\left( -1 \right)\times \left( 1 \right)$
Thus, $\sin \left( \dfrac{11\pi }{2} \right)=-1$
Note: One must remember the basic values of sin and cos, it is very common to make mistakes in the signs for +1 and -1 when using the values of sin and cos. Another common mistake is to make sign mistakes in the \[sin\left( a+b \right)\] formula.
Alternatively, one can directly see that $\dfrac{11\pi }{2}$ directly is of the form $\sin \left( \dfrac{\left( 4n+3 \right)\pi }{2} \right)$ and thus it would be equal to -1.
You can also look at the graph and to see the value.
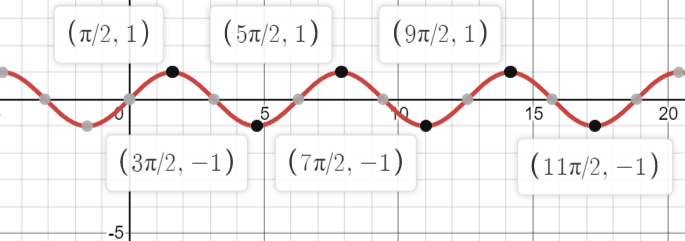
Complete step by step answer:
This type of question is mainly asked to check whether one remembers the formula $\sin (a+b)=\sin a\cos b+\sin b\cos a$ and the values of sin and cos at $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and $n\pi $ .
We know, $\sin (n\pi )$ is 0 for all n belonging to integers, $\sin \left( \dfrac{(4n+1)\pi }{2} \right)$ is 1 for all n belonging to integers, $\cos \left( \dfrac{\left( 2n+1 \right)\pi }{2} \right)$ is 0 for all n belonging to integers and $\cos \left( \left( 2n+1 \right)\pi \right)$ is -1 for all n belonging to integers.
We know, $\dfrac{11\pi }{2}=\dfrac{10\pi +\pi }{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{11\pi }{2}=\dfrac{10\pi }{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Since 10 is divisible by 2 and when dividing 10 by 2 we get 5,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{10\pi }{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{2}=5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
Thus, $\sin \left( \dfrac{11\pi }{2} \right)=\sin \left( 5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$
Now, taking a as $5\pi $ and b as $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and applying it in the formula of $\sin (a+b)=\sin a\cos b+\sin b\cos a$ we have,
$\sin \left( 5\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\sin \left( 5\pi \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)+\cos \left( 5\pi \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ .
$\sin \left( 5\pi \right)$ is of the form $\sin \left( n\pi \right)$ so equal to 0 , $\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ is of the form $\sin \left( \dfrac{(4n+1)\pi }{2} \right)$ so equal to 1 , $\cos \left( 5\pi \right)$ is of the form $\cos \left( \left( 2n+1 \right)\pi \right)$ so equal to -1 and $\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)$ is of the form $\cos \left( \dfrac{\left( 2n+1 \right)\pi }{2} \right)$ so equal to 0.
$\Rightarrow \sin \left( 5\pi \right)\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)+\cos \left( 5\pi \right)\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=0\times 0+\left( -1 \right)\times \left( 1 \right)$
Thus, $\sin \left( \dfrac{11\pi }{2} \right)=-1$
Note: One must remember the basic values of sin and cos, it is very common to make mistakes in the signs for +1 and -1 when using the values of sin and cos. Another common mistake is to make sign mistakes in the \[sin\left( a+b \right)\] formula.
Alternatively, one can directly see that $\dfrac{11\pi }{2}$ directly is of the form $\sin \left( \dfrac{\left( 4n+3 \right)\pi }{2} \right)$ and thus it would be equal to -1.
You can also look at the graph and to see the value.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

What is the difference between biodegradable and nonbiodegradable class 11 biology CBSE

Proton was discovered by A Thomson B Rutherford C Chadwick class 11 chemistry CBSE




