
When ethanamide is treated with $EtMgBr$, followed by hydrolysis, the product is:
(A)
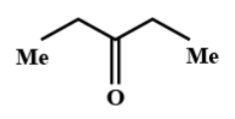
(B)
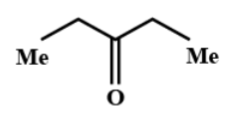
(C)
(D)




Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: A Grignard reagent allows us to take any hydrocarbyl halide, metallate it, and when it tends to react with a carbonyl compound it will form carbon-carbon bonds straightforwardly and directly. When it reacts with an amide, on hydrolysis it will try to form an ether.
Complete step by step solution:
As per the given question, ethanamide (with chemical formula $C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}$) reacts with $EtMgBr$ that is ethyl magnesium bromide, which is a Grignard reagent and it also undergoes hydrolysis. So, to find out the product let us see what is the Grignard reaction and what is the mechanism of the reaction.
So, the Grignard reaction, discovered by Francois Auguste Victor Grignard refers to an organometallic chemical reaction where groups like alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides when are added to a carbonyl group tends to form carbon-carbon bond.
Grignard reagent is highly nucleophilic in nature. So, this reagent will generally attack the electrophilic carbon in the polar bond of the carbonyl group and will further tend to form a carbon-carbon bond structure.
Thus, here considering the Methyl group in ethanamide as the $R$ group and the methyl group in $EtMgBr$ as the $R'$group, when it is hydrolysed it tends to form a ketone and eliminates the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ group. So, the reaction will be like as shown in the below figure:
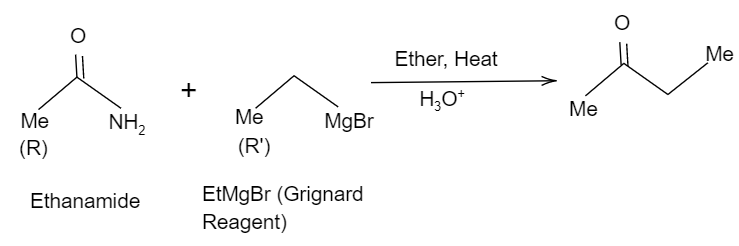
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The reaction of alkyl or aryl halides gives the Grignard reagent as product and is generally used for the synthesis of aldehydes and ketones (especially). The Grignard reaction is also used for the synthesis of carbon-carbon bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
As per the given question, ethanamide (with chemical formula $C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}$) reacts with $EtMgBr$ that is ethyl magnesium bromide, which is a Grignard reagent and it also undergoes hydrolysis. So, to find out the product let us see what is the Grignard reaction and what is the mechanism of the reaction.
So, the Grignard reaction, discovered by Francois Auguste Victor Grignard refers to an organometallic chemical reaction where groups like alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides when are added to a carbonyl group tends to form carbon-carbon bond.
Grignard reagent is highly nucleophilic in nature. So, this reagent will generally attack the electrophilic carbon in the polar bond of the carbonyl group and will further tend to form a carbon-carbon bond structure.
Thus, here considering the Methyl group in ethanamide as the $R$ group and the methyl group in $EtMgBr$ as the $R'$group, when it is hydrolysed it tends to form a ketone and eliminates the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ group. So, the reaction will be like as shown in the below figure:

Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The reaction of alkyl or aryl halides gives the Grignard reagent as product and is generally used for the synthesis of aldehydes and ketones (especially). The Grignard reaction is also used for the synthesis of carbon-carbon bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




