
Etard's reaction involves the preparation of Benzaldehyde from:
(A) Toluene
(B) Ethyl benzene
(C) Benzoyl chloride
(D) Sodium benzoate
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: Etard’s reaction involves oxidation of a methyl group attached to an aromatic system with Chromyl chloride reagent. This reaction yields corresponding aldehyde as a main product.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s see the basics about the Etard reaction.
- Etard's reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the direct oxidation of an aromatic methyl group to an aldehyde using chromyl chloride.
- Chromyl chloride is used as an oxidising agent in this reaction. Chromium metal is in +6 oxidation state in Chromyl chloride, so it can oxidise other compounds.
- This reaction is important in synthetic organic chemistry because it oxidises methyl group to –CHO while other oxidising agents directly oxidise it to –COOH group only. Such as $KMn{{O}_{4}},{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$ oxidises methyl group directly to the corresponding carboxylic acid.
- The mechanism of this reaction involves a reaction followed by sigmatropic rearrangement.
For example, Toluene can be oxidized to benzaldehyde by Etard reaction.
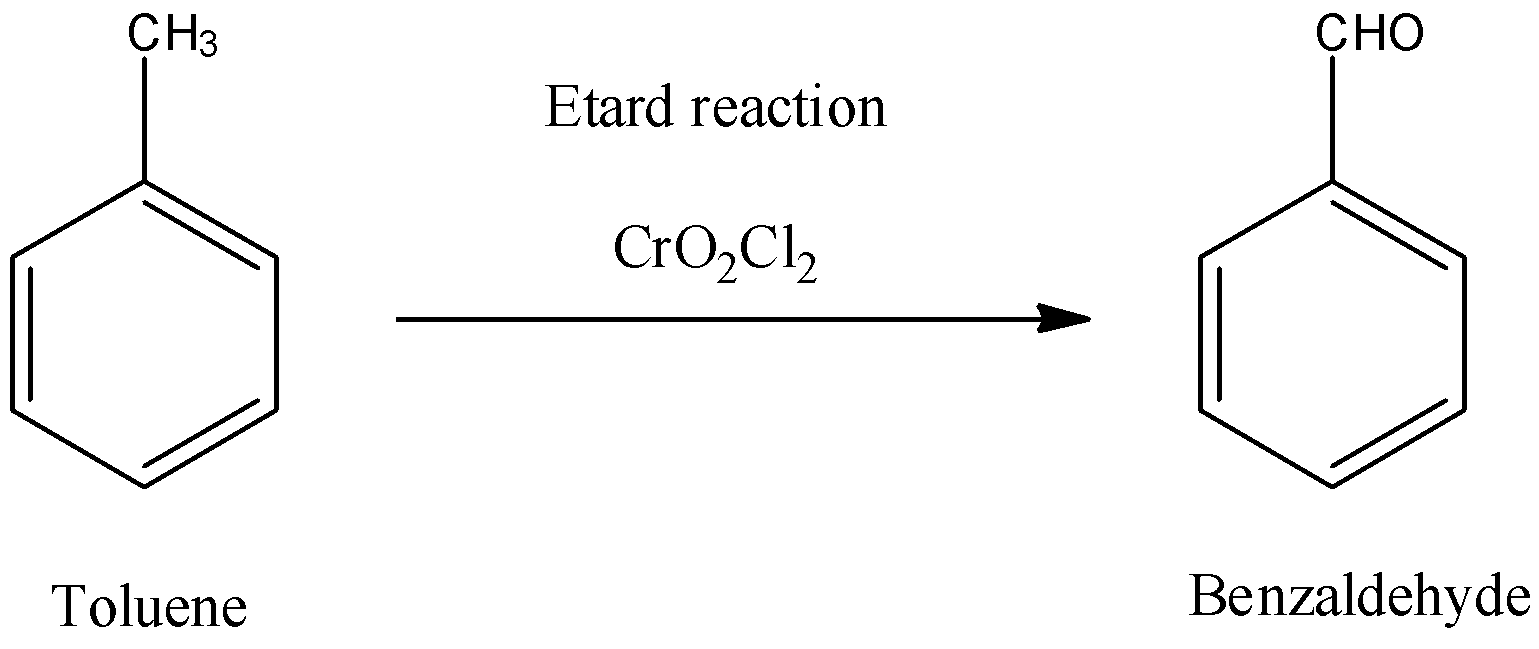
-Here, we can see that the methyl group of toluene is an aromatic methyl group and so it can be oxidised by Chromyl chloride to corresponding aldehydes. If a methyl group is attached to any aromatic heterocyclic ring, then also this reaction is possible. So, when toluene will react with Chromyl chloride, it will give benzaldehyde as a main product.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Remember that if an ethyl group or any other alkyl chain other than methyl is attached to the aromatic ring, then it cannot give aldehyde as a product. Instead, they will give ketone products with ketone group on the carbon which is directly attached with an aromatic ring.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s see the basics about the Etard reaction.
- Etard's reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the direct oxidation of an aromatic methyl group to an aldehyde using chromyl chloride.
- Chromyl chloride is used as an oxidising agent in this reaction. Chromium metal is in +6 oxidation state in Chromyl chloride, so it can oxidise other compounds.
- This reaction is important in synthetic organic chemistry because it oxidises methyl group to –CHO while other oxidising agents directly oxidise it to –COOH group only. Such as $KMn{{O}_{4}},{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$ oxidises methyl group directly to the corresponding carboxylic acid.
- The mechanism of this reaction involves a reaction followed by sigmatropic rearrangement.
For example, Toluene can be oxidized to benzaldehyde by Etard reaction.

-Here, we can see that the methyl group of toluene is an aromatic methyl group and so it can be oxidised by Chromyl chloride to corresponding aldehydes. If a methyl group is attached to any aromatic heterocyclic ring, then also this reaction is possible. So, when toluene will react with Chromyl chloride, it will give benzaldehyde as a main product.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Remember that if an ethyl group or any other alkyl chain other than methyl is attached to the aromatic ring, then it cannot give aldehyde as a product. Instead, they will give ketone products with ketone group on the carbon which is directly attached with an aromatic ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




