
Etard reaction in the following is:
A.Oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by chromyl chloride
B.Oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by alkaline $KMn{O_4}$
C.Dry distillation of calcium benzoate
D.Reaction of benzene with $C{l_2}$ in the presence of UV light
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: We must know that the direct oxidation of an aromatic bound methyl group to an aldehyde in the presence of chromyl chloride is Etard Reaction. We know it provides a way for the oxidation of aromatic methyl groups. We could produce aldehydes by partial oxidation, and so we use chromyl chloride as it is a weak oxidizing agent.
Complete step by step answer:
The direct method of obtaining an aldehyde by partial oxidation of aromatic methylated compounds in the presence of chromyl chloride is called Etard reaction.
The reaction begins with formation of a precipitated Etard complex, which is obtained via an ene reaction with chromyl chloride. The decomposition of Etard complex is done by [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement under reducing conditions to stop further oxidation to take place for the formation of carboxylic acid. Saturated aqueous solutions such as sodium sulfite provide the reducing conditions for the decomposition of the Etard complex.
We can use solvents such as carbon disulfide, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride and dichloromethane.
An example of Etard’s reaction from the given option is oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde using chromyl chloride.
Toluene reacts with chromyl chloride in the presence of non-polar solvents such as carbon tetrachloride to form benzaldehyde.
We are using chromyl chloride because it is a weak oxidizing agent. Chromyl chloride changes the methyl group to form a chromium complex. The chromium complex undergoes acid hydrolysis to form benzaldehyde.
\[
{C_6}{H_5}C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{Cr{O_2}C{l_2}}}{C_6}{H_5}CH{\left( {OCrOHC{l_2}} \right)_2}\xrightarrow{{{H_2}O}}{C_6}{H_5}CHO \\
Toluene\,\,\,\,\,Chromyl\,\,\,Chromium\,complex\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Benzaldehyde \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,chloride \\
\]
We can write the chemical reaction as,
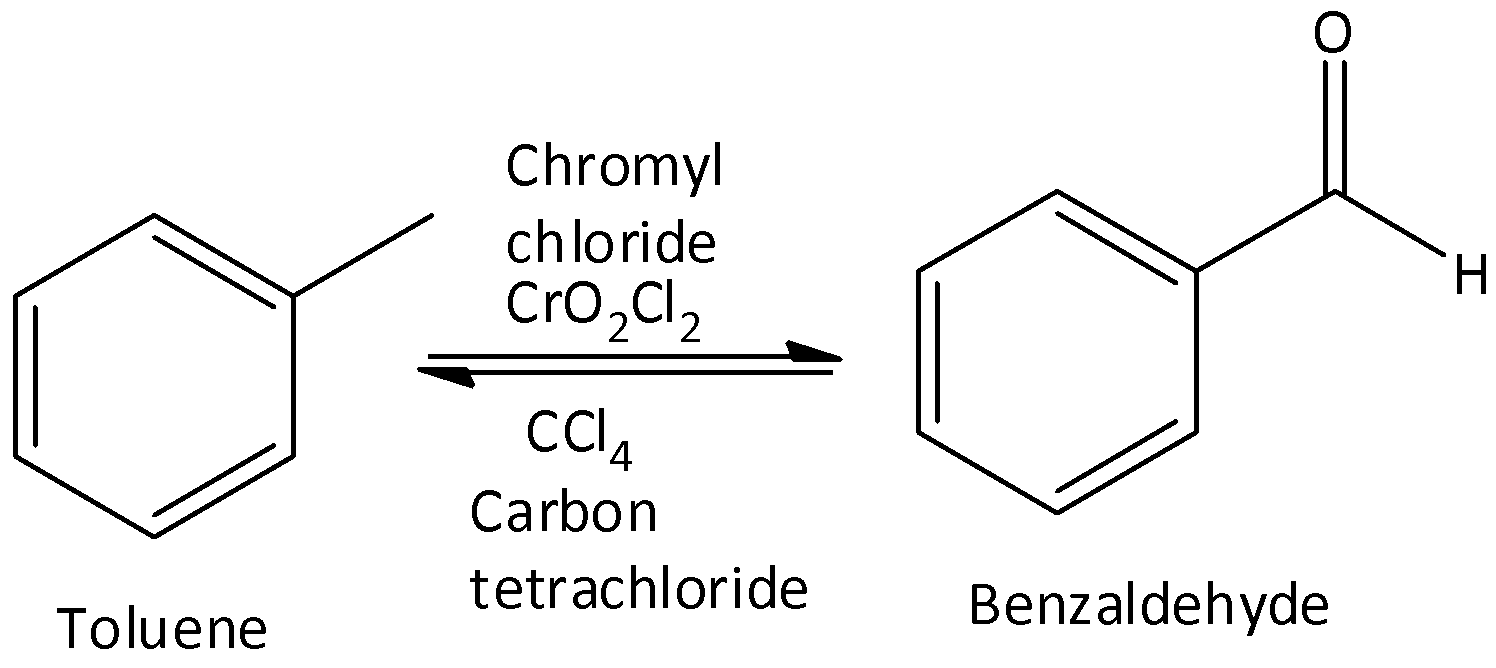
$\therefore $ Option (A) is correct.
Note:
If we use a strong oxidizing agent in the Etard reaction, the product of the reaction would be stable carboxylic acids. We cannot use strong oxidizing agents such as potassium permanganate because it could completely oxidize toluene to benzoic acid (carboxylic acid). If we want a highly pure product of aldehyde, we have to purify the complex precipitate before decomposing it, so that any unreacted reagent would be removed. We can use benzaldehyde as a reagent in preparing dyes, pharmaceuticals and perfumes. Chlorination of benzene in the presence of UV light is an additional reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The direct method of obtaining an aldehyde by partial oxidation of aromatic methylated compounds in the presence of chromyl chloride is called Etard reaction.
The reaction begins with formation of a precipitated Etard complex, which is obtained via an ene reaction with chromyl chloride. The decomposition of Etard complex is done by [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement under reducing conditions to stop further oxidation to take place for the formation of carboxylic acid. Saturated aqueous solutions such as sodium sulfite provide the reducing conditions for the decomposition of the Etard complex.
We can use solvents such as carbon disulfide, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride and dichloromethane.
An example of Etard’s reaction from the given option is oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde using chromyl chloride.
Toluene reacts with chromyl chloride in the presence of non-polar solvents such as carbon tetrachloride to form benzaldehyde.
We are using chromyl chloride because it is a weak oxidizing agent. Chromyl chloride changes the methyl group to form a chromium complex. The chromium complex undergoes acid hydrolysis to form benzaldehyde.
\[
{C_6}{H_5}C{H_3}\xrightarrow{{Cr{O_2}C{l_2}}}{C_6}{H_5}CH{\left( {OCrOHC{l_2}} \right)_2}\xrightarrow{{{H_2}O}}{C_6}{H_5}CHO \\
Toluene\,\,\,\,\,Chromyl\,\,\,Chromium\,complex\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,Benzaldehyde \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,chloride \\
\]
We can write the chemical reaction as,

$\therefore $ Option (A) is correct.
Note:
If we use a strong oxidizing agent in the Etard reaction, the product of the reaction would be stable carboxylic acids. We cannot use strong oxidizing agents such as potassium permanganate because it could completely oxidize toluene to benzoic acid (carboxylic acid). If we want a highly pure product of aldehyde, we have to purify the complex precipitate before decomposing it, so that any unreacted reagent would be removed. We can use benzaldehyde as a reagent in preparing dyes, pharmaceuticals and perfumes. Chlorination of benzene in the presence of UV light is an additional reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




