
Establish expression for refractive index of material of prism.
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint:Snell’s law gives us the correlation among incidence angle and emergence angle when a ray of light is allowed to pass through a medium. We will be using the expression of Snell’s law to find the expression for the refractive index of the material of the given prism.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider a triangular prism ABC having two refracting surfaces. A ray of light is an incident of refracting surface AB called an incident ray, and it leaves the prism as represented by QR called an emergent ray. PN and QN are normal to refracting surface AB and AC, respectively.
Assume:
The angle between normal PN and incident ray is denoted by \[{i_1}\].
The angle between normal QN and emergent ray is denoted by \[{i_2}\].
\[{\delta _1}\] is the angle between PM and PQ and \[{\delta _2}\] is the angle between MQ and PQ.\[{r_1}\] is the angle between PN and PQ and \[{r_2}\] is the angle between QN and PQ.The angle between MQ and ML is the angle of deviation and denoted by \[\delta \].
A is the angle of the prism.
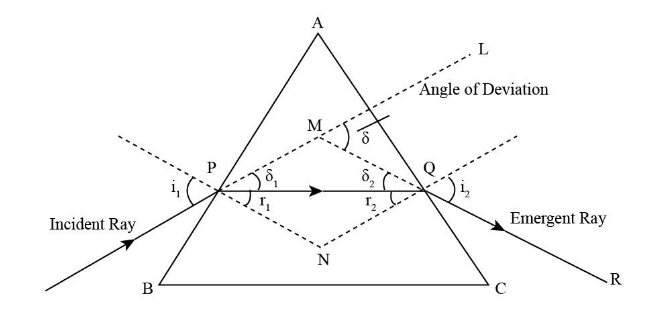
For triangle APQ, we can see that angle of prism is equal to the summation of \[\angle {r_1}\] and \[\angle {r_2}\] so we can write:
\[A = {r_1} + {r_2}\]……(1)
We know that if there is a minimum deviation case then \[\angle {r_1}\]and \[\angle {r_2}\] are equal, we can assume them equal to an angle r.
\[\begin{array}{l}
{r_1} = {r_2}\\ = r\end{array}\]
Substitute \[r\] for \[{r_1}\] and \[{r_2}\] in equation (1).
\[\begin{array}{l}
A = r + r\\
r = \dfrac{A}{2}
\end{array}\]
We also know that the summation of prism and angle of deviation is equal to the summation of angle of incidence \[{i_1}\] and angle of emergence \[{i_2}\] for minimum deviation.
\[A + {\delta _m} = {i_1} + {i_2}\]......(2)
Here \[{\delta _m}\] is the angle of minimum deviation.
Again, we know that angle of incidence and angle of emergence are equal for minimum deviation so we can assume them equal to an angle i.
\[\begin{array}{l}
{i_1} = {i_2}\\ = i\end{array}\]
On substituting i for \[{i_2}\] and \[{i_2}\] in equation (2), we get:
\[\begin{array}{l}
A + {\delta _m} = i + i\\
i = \dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}
\end{array}\]
Using the concept of Snell’s rule, we can write:
\[\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}\]
Here \[\mu \] is the refractive index of the prism.
On substituting \[\dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}\] for i and \[\dfrac{A}{2}\] for r in the above expression, we get:
\[\mu = \dfrac{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}} \right)}}{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}}\]
Therefore, the expression for the refractive index of the material of prism is given by the expression \[\mu = \dfrac{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}} \right)}}{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}}\].
Note: Alternate method: We can also use different trigonometry methods to find the relation between various angles to find the expression for angle of incidence ray and angle of emergence ray. In the end, we can substitute their values in the expression of Snell’s law as above.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider a triangular prism ABC having two refracting surfaces. A ray of light is an incident of refracting surface AB called an incident ray, and it leaves the prism as represented by QR called an emergent ray. PN and QN are normal to refracting surface AB and AC, respectively.
Assume:
The angle between normal PN and incident ray is denoted by \[{i_1}\].
The angle between normal QN and emergent ray is denoted by \[{i_2}\].
\[{\delta _1}\] is the angle between PM and PQ and \[{\delta _2}\] is the angle between MQ and PQ.\[{r_1}\] is the angle between PN and PQ and \[{r_2}\] is the angle between QN and PQ.The angle between MQ and ML is the angle of deviation and denoted by \[\delta \].
A is the angle of the prism.

For triangle APQ, we can see that angle of prism is equal to the summation of \[\angle {r_1}\] and \[\angle {r_2}\] so we can write:
\[A = {r_1} + {r_2}\]……(1)
We know that if there is a minimum deviation case then \[\angle {r_1}\]and \[\angle {r_2}\] are equal, we can assume them equal to an angle r.
\[\begin{array}{l}
{r_1} = {r_2}\\ = r\end{array}\]
Substitute \[r\] for \[{r_1}\] and \[{r_2}\] in equation (1).
\[\begin{array}{l}
A = r + r\\
r = \dfrac{A}{2}
\end{array}\]
We also know that the summation of prism and angle of deviation is equal to the summation of angle of incidence \[{i_1}\] and angle of emergence \[{i_2}\] for minimum deviation.
\[A + {\delta _m} = {i_1} + {i_2}\]......(2)
Here \[{\delta _m}\] is the angle of minimum deviation.
Again, we know that angle of incidence and angle of emergence are equal for minimum deviation so we can assume them equal to an angle i.
\[\begin{array}{l}
{i_1} = {i_2}\\ = i\end{array}\]
On substituting i for \[{i_2}\] and \[{i_2}\] in equation (2), we get:
\[\begin{array}{l}
A + {\delta _m} = i + i\\
i = \dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}
\end{array}\]
Using the concept of Snell’s rule, we can write:
\[\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}\]
Here \[\mu \] is the refractive index of the prism.
On substituting \[\dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}\] for i and \[\dfrac{A}{2}\] for r in the above expression, we get:
\[\mu = \dfrac{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}} \right)}}{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}}\]
Therefore, the expression for the refractive index of the material of prism is given by the expression \[\mu = \dfrac{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}} \right)}}{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}}\].
Note: Alternate method: We can also use different trigonometry methods to find the relation between various angles to find the expression for angle of incidence ray and angle of emergence ray. In the end, we can substitute their values in the expression of Snell’s law as above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




