
Equation of a circle passing through origin and cuts off intercepts equal to 3 and 4 from the positive \[x\]-axis and \[y\]-axis respectively.
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint:
First, we will find the midpoint of the points on –axis and –axis on the circle and the centre of the circle. Then, we will find the radius of the circle using the distance formula between the given points. Then the values are substituted in the equation of the circle with centre \[\left( {a,b} \right)\] and having radius \[r\] is given by \[{\left( {x - a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - b} \right)^2} = {r^2}\] to find the required equation.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that the circle passes through origin O.
Now, we will take the points on \[x\]–axis and \[y\]–axis which are intersected by the circle are \[{\text{A}}\left( {3,0} \right)\] and \[{\text{B}}\left( {0,4} \right)\] respectively.
So, the mid-points of \[{\text{O}}\left( {0,0} \right)\] and \[{\text{A}}\left( {3,0} \right)\] is \[{\text{C}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{2},0} \right)\] and of \[{\text{O}}\left( {0,0} \right)\] and \[{\text{B}}\left( {0,4} \right)\] is \[{\text{D}}\left( {0,2} \right)\].
\[{x_2} = 2\]
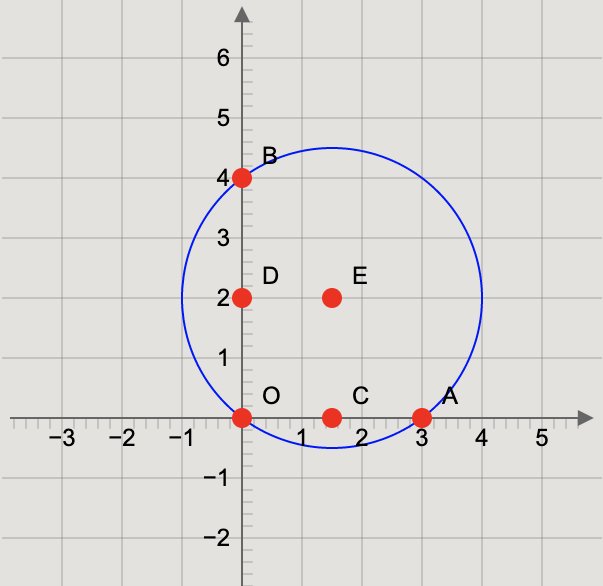
From the above figure, we get that the centre of the circle is \[{\text{E}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{2},2} \right)\].
We know that the radius of the circle is the distance between the centre \[\left( {\dfrac{3}{2},2} \right)\] and point on the circle \[\left( {0,0} \right)\].
Since we know that the distance between the two points \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)}^2}} \].
We will now find the radius of the circle \[r\] using the above distance formula with \[{x_1} = \dfrac{3}{2}\], \[{y_1} = 0\], and \[{y_2} = 0\].
\[
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2} - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - 0} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^2} + {2^2}} \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {\dfrac{9}{4} + 4} \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{25}}{4}} \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{5}{2} \\
\]
We know that the equation of the circle with centre \[\left( {a,b} \right)\] and having radius \[r\] is given by \[{\left( {x - a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - b} \right)^2} = {r^2}\].
Substituting these values in the above equation of circle, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\left( {x - \dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 2} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + \dfrac{9}{4} - 3x + {y^2} + 4 - 4y = \dfrac{{25}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y + \dfrac{{25}}{4} = \dfrac{{25}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y + 0 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y = 0 \\
\]
Therefore, the equation of the circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y = 0\].
Note:
We can also rephrase this question to find the equation of diameter of a circle that passes through the origin and the equation of a family of circles passing through two points. Also, we will verify this solution by substituting the value of the centre of the circle \[\left( {a,b} \right)\] in the equation \[{x^2} + {y^2} - ax - by = 0\].
Replacing 3 for \[x\] and 4 for \[y\] in the above equation, we get
\[{x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y = 0\]
Hence, our solution is correct.
First, we will find the midpoint of the points on –axis and –axis on the circle and the centre of the circle. Then, we will find the radius of the circle using the distance formula between the given points. Then the values are substituted in the equation of the circle with centre \[\left( {a,b} \right)\] and having radius \[r\] is given by \[{\left( {x - a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - b} \right)^2} = {r^2}\] to find the required equation.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that the circle passes through origin O.
Now, we will take the points on \[x\]–axis and \[y\]–axis which are intersected by the circle are \[{\text{A}}\left( {3,0} \right)\] and \[{\text{B}}\left( {0,4} \right)\] respectively.
So, the mid-points of \[{\text{O}}\left( {0,0} \right)\] and \[{\text{A}}\left( {3,0} \right)\] is \[{\text{C}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{2},0} \right)\] and of \[{\text{O}}\left( {0,0} \right)\] and \[{\text{B}}\left( {0,4} \right)\] is \[{\text{D}}\left( {0,2} \right)\].
\[{x_2} = 2\]

From the above figure, we get that the centre of the circle is \[{\text{E}}\left( {\dfrac{3}{2},2} \right)\].
We know that the radius of the circle is the distance between the centre \[\left( {\dfrac{3}{2},2} \right)\] and point on the circle \[\left( {0,0} \right)\].
Since we know that the distance between the two points \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)}^2}} \].
We will now find the radius of the circle \[r\] using the above distance formula with \[{x_1} = \dfrac{3}{2}\], \[{y_1} = 0\], and \[{y_2} = 0\].
\[
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2} - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {2 - 0} \right)}^2}} \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^2} + {2^2}} \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {\dfrac{9}{4} + 4} \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt {\dfrac{{25}}{4}} \\
\Rightarrow r = \dfrac{5}{2} \\
\]
We know that the equation of the circle with centre \[\left( {a,b} \right)\] and having radius \[r\] is given by \[{\left( {x - a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - b} \right)^2} = {r^2}\].
Substituting these values in the above equation of circle, we get
\[
\Rightarrow {\left( {x - \dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 2} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + \dfrac{9}{4} - 3x + {y^2} + 4 - 4y = \dfrac{{25}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y + \dfrac{{25}}{4} = \dfrac{{25}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y + 0 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y = 0 \\
\]
Therefore, the equation of the circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y = 0\].
Note:
We can also rephrase this question to find the equation of diameter of a circle that passes through the origin and the equation of a family of circles passing through two points. Also, we will verify this solution by substituting the value of the centre of the circle \[\left( {a,b} \right)\] in the equation \[{x^2} + {y^2} - ax - by = 0\].
Replacing 3 for \[x\] and 4 for \[y\] in the above equation, we get
\[{x^2} + {y^2} - 3x - 4y = 0\]
Hence, our solution is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




