
Epoxides are:
A. Unsaturated ethers
B. Mixed ethers
C. Cyclic ethers
D. None of these
Answer
373.8k+ views
Hint: An epoxide is a type of ether with a three-atom ring. This ring resembles an equilateral triangle and is therefore strained. This is formed by the oxidation reaction of unsaturated hydrocarbon alkenes.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
An epoxide is a cyclic structure having an ether functional group.
It has a three-atom ring.
The general structure of epoxide is as follows:
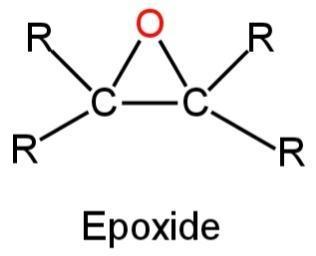
Image: Epoxide.
The simplest epoxide is ethylene oxide.
It is also known as oxirane.
The structure of ethylene oxide is as follows:
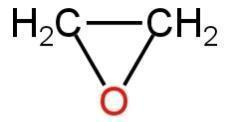
Image: Structure of ethylene oxide.
This is a simple epoxide which is a three-membered ring including one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms.
The atoms are connected through sigma bonds.
Ethylene oxide is the epoxide of ethylene
Epoxides have a strained ring, as a result, it readily carries out various additional reactions for the process of ring-opening.
Epoxides are colourless.
The preparation of epoxide involves the ethylene molecule undergoing oxidation at a fixed temperature.
Silver enhances the speed of the reaction by acting as a catalyst.
Let us consider the example of the formation of the simplest epoxide i.e., ethylene oxide from ethene.
The reaction happens as comes next:
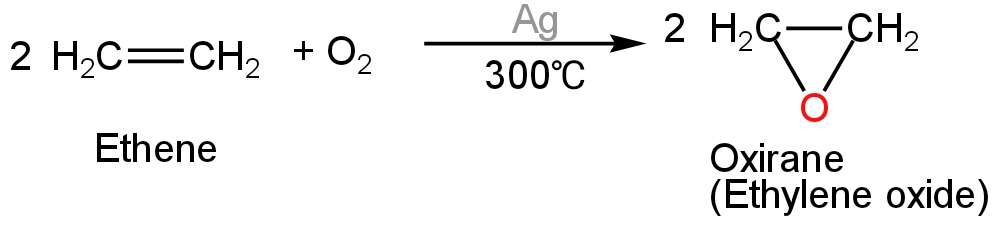
Image: production of an epoxide.
Similarly, propylene oxide is formed from the reaction of propylene with oxygen.
Apart from this process of production, most epoxides are yielded by the reaction of alkenes with peroxide reagents, which contribute to a single oxygen atom.
Ethylene oxide is utilised to develop detergents and surfactants.
It is also used for the sterilisation of medical devices and objects.
So, option A is correct.
Note: Epoxides react with a wide spectrum of nucleophiles like alcohols, water, amines, thiols, and halides. Due to the difference in the electronegativity of carbon and oxygen, oxygen has a partial negative charge and carbon has a partial positive charge. Epoxides have two electrophilic carbon available for attack by the nucleophile so are ambident substrates.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
An epoxide is a cyclic structure having an ether functional group.
It has a three-atom ring.
The general structure of epoxide is as follows:

Image: Epoxide.
The simplest epoxide is ethylene oxide.
It is also known as oxirane.
The structure of ethylene oxide is as follows:

Image: Structure of ethylene oxide.
This is a simple epoxide which is a three-membered ring including one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms.
The atoms are connected through sigma bonds.
Ethylene oxide is the epoxide of ethylene
Epoxides have a strained ring, as a result, it readily carries out various additional reactions for the process of ring-opening.
Epoxides are colourless.
The preparation of epoxide involves the ethylene molecule undergoing oxidation at a fixed temperature.
Silver enhances the speed of the reaction by acting as a catalyst.
Let us consider the example of the formation of the simplest epoxide i.e., ethylene oxide from ethene.
The reaction happens as comes next:

Image: production of an epoxide.
Similarly, propylene oxide is formed from the reaction of propylene with oxygen.
Apart from this process of production, most epoxides are yielded by the reaction of alkenes with peroxide reagents, which contribute to a single oxygen atom.
Ethylene oxide is utilised to develop detergents and surfactants.
It is also used for the sterilisation of medical devices and objects.
So, option A is correct.
Note: Epoxides react with a wide spectrum of nucleophiles like alcohols, water, amines, thiols, and halides. Due to the difference in the electronegativity of carbon and oxygen, oxygen has a partial negative charge and carbon has a partial positive charge. Epoxides have two electrophilic carbon available for attack by the nucleophile so are ambident substrates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




