
What energy conversion takes place in a generator when it is in use?
A) Electrical energy changes to electrical energy.
B) Mechanical energy changes to mechanical energy.
C) Electrical energy changes to mechanical energy.
D) Mechanical energy changes to electrical energy.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: An electric generator can be an AC generator or a DC generator. The working of a generator is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction where a change in the magnetic flux associated with a conductor induces an electric current in it. Sketching the setup involved in a generator and accounting for its working will help us determine the conversion of energy involved in it.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1: Sketch a figure representing the diagram for the working of an electric generator.
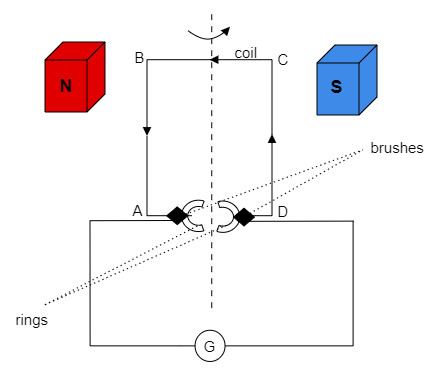
In the above figure, a conductor coil ABCD is placed between two poles – north pole and south pole of two magnets. The two half rings are attached to two brushes. The brushes are connected to a galvanometer to record the current generated.
Step 2: Try to explain the working of an electric generator.
The two poles will generate a magnetic field which then causes the loop ABCD to rotate. First side AB will be facing upwards and side CD will be facing downwards. The rotation of the loop causes the magnetic flux linked with the coil to change. The change in magnetic flux then induces an electric current. The direction of the current as determined by Flemming’s left-hand rule takes the path B-A-G-D-C. The half rings are insulated from each other and can slide while the brushes try to remain in contact as the loop rotates. Here the current produced is direct.
Since it is the rotation of the loop that generates an electric current in a generator, mechanical energy gets converted to electrical energy.
So the correct option is D.
Note: A dc generator produces a direct current where the direction of the current remains the same for a full rotation of the loop. An ac generator produces an alternating current where the direction of the current will change in every half rotation of the loop. For an ac generator, we use full rings instead of half rings.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1: Sketch a figure representing the diagram for the working of an electric generator.

In the above figure, a conductor coil ABCD is placed between two poles – north pole and south pole of two magnets. The two half rings are attached to two brushes. The brushes are connected to a galvanometer to record the current generated.
Step 2: Try to explain the working of an electric generator.
The two poles will generate a magnetic field which then causes the loop ABCD to rotate. First side AB will be facing upwards and side CD will be facing downwards. The rotation of the loop causes the magnetic flux linked with the coil to change. The change in magnetic flux then induces an electric current. The direction of the current as determined by Flemming’s left-hand rule takes the path B-A-G-D-C. The half rings are insulated from each other and can slide while the brushes try to remain in contact as the loop rotates. Here the current produced is direct.
Since it is the rotation of the loop that generates an electric current in a generator, mechanical energy gets converted to electrical energy.
So the correct option is D.
Note: A dc generator produces a direct current where the direction of the current remains the same for a full rotation of the loop. An ac generator produces an alternating current where the direction of the current will change in every half rotation of the loop. For an ac generator, we use full rings instead of half rings.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




