
Elements up to atomic number 112 have been discovered till now. What will be the electronic configuration of the element possessing atomic number 108.
A) $[Rn]5{f^{14}}6{d^6}7{s^2}$
B) $6{f^{14}}7{d^8}7{s^2}$
C) $[Rn]5{f^{14}}6{d^6}7{s^0}$
D) $[Xe]4{f^{14}}5{d^8}6{s^2}$
Answer
494.4k+ views
Hint: To find the electronic configuration we will have to know about the Aufbau Principle. To find out the condensed electron configuration, the configuration of the nearest Noble gas is considered followed by filling the remaining electrons into the shells.
Complete answer:
The Aufbau principle was named after the word ‘Aufbeen’. According to this principle the electrons are filled according to the energies of the orbitals, meaning that the orbitals with lower energies are filled first and then the higher energy one’s are filled. The energy of an orbital can be determined as the sum of principle and the azimuthal quantum numbers of that orbital. According to this, the order in which the electrons are filled in the orbitals is: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p…
The order can be conveniently represented by the image below:
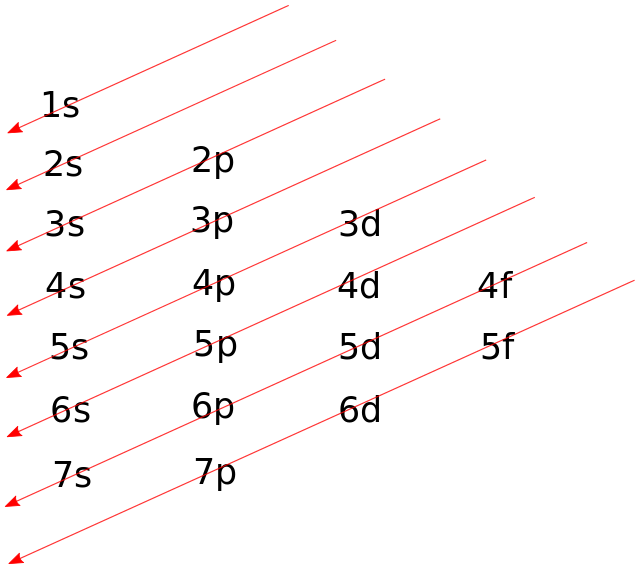
We have to find the electronic configuration of an element having atomic number 108. Hence, we can say that the element contains 108 electrons. First we’ll find the nearest Noble gas to this atomic number, which is Radon (At. No = 86). The condensed molecular formula can be written wrt to the Radon atom. The electronic configuration of Radon is: $[Xe]4{f^{14}}5{d^{10}}6{s^2}6{p^6}$
The difference in the no. of electrons between Radon and given element is: $108 - 86 = 22$
Hence in the condensed formula we’ll have to add 22 electrons after Radon. From the Aufbau Principle the orbital filling after 6p is 7s. After that 5f,6d will be filled. The final electronic configuration of given element is: $E.C = [Rn]7{s^2}5{f^{14}}6{d^6}$
The correct answer is Option (A).
Note:
The given element belongs to the d-block as the last electron enters the d shell. The group no. of a d-block element can be given as: $no.of{\text{ }}electron\operatorname{s} {\text{ }}in{\text{ }}(n - 1)d{\text{ }}shell + no.of{\text{ }}electron\operatorname{s} {\text{ }}in{\text{ }}s{\text{ }}subshell$
The group no. of the given element $ = 4 + 2 = 6$
Complete answer:
The Aufbau principle was named after the word ‘Aufbeen’. According to this principle the electrons are filled according to the energies of the orbitals, meaning that the orbitals with lower energies are filled first and then the higher energy one’s are filled. The energy of an orbital can be determined as the sum of principle and the azimuthal quantum numbers of that orbital. According to this, the order in which the electrons are filled in the orbitals is: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p…
The order can be conveniently represented by the image below:

We have to find the electronic configuration of an element having atomic number 108. Hence, we can say that the element contains 108 electrons. First we’ll find the nearest Noble gas to this atomic number, which is Radon (At. No = 86). The condensed molecular formula can be written wrt to the Radon atom. The electronic configuration of Radon is: $[Xe]4{f^{14}}5{d^{10}}6{s^2}6{p^6}$
The difference in the no. of electrons between Radon and given element is: $108 - 86 = 22$
Hence in the condensed formula we’ll have to add 22 electrons after Radon. From the Aufbau Principle the orbital filling after 6p is 7s. After that 5f,6d will be filled. The final electronic configuration of given element is: $E.C = [Rn]7{s^2}5{f^{14}}6{d^6}$
The correct answer is Option (A).
Note:
The given element belongs to the d-block as the last electron enters the d shell. The group no. of a d-block element can be given as: $no.of{\text{ }}electron\operatorname{s} {\text{ }}in{\text{ }}(n - 1)d{\text{ }}shell + no.of{\text{ }}electron\operatorname{s} {\text{ }}in{\text{ }}s{\text{ }}subshell$
The group no. of the given element $ = 4 + 2 = 6$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




