
What is the electric potential at the center of the triangle as shown in figure.
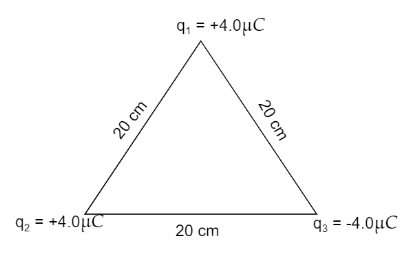

Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint: We will first find the center of the triangle by drawing perpendicular lines from each corner of the triangle. When we get the distance of the centre from each vertex of the triangle then we can find the electric potential due to each charge placed at the vertices of the triangle. The equivalent electric potential at the centre will be the sum of electric potential due to each charge placed at vertices of the triangle.
Formula Used:
Electric potential \[ = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{kQ}}{r}\]
Where, \[k = \] Electric constant, \[Q = \] Electric charge and \[r = \] Distance of point from charge $Q$.
Complete step by step answer:
For finding electric potential at the centre of the triangle we need to find the distance of the centre from each vertex of the triangle. Let’s mark this distance as \[x\].Also for finding the position of the centre of a triangle we make perpendicular lines from each vertex. The point where each perpendicular meet is the centre of the triangle. Let’s name this centre of the triangle as C.
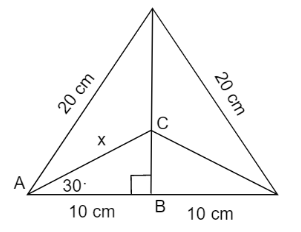
Since it is an equilateral triangle, therefore each angle of the triangle will be of \[{60^ \circ }\], therefore \[\angle {\text{CAB = 3}}{0^ \circ }\]. Now in \[\Delta ABC\] we can apply, \[\cos 30{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{10}}{x}\] , because we know that the cosine of angle is the ratio of base and hypotenuse.
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{ }}\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{10}}{x}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{ x = }}\dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ cm}}\]
Now we will find electric potential due to each charge placed at vertex of triangle at the centre of triangle which is at a distance of \[{\text{ }}\dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ cm}}\]. We know that potential is a vector quantity, therefore the electric potential at centre will be the sum of individual potential at centre. Therefore it can calculated as:
\[{V_{net}}{\text{ = }}{V_{ + 4\mu C}}{\text{ + }}{V_{ + 4\mu C}}{\text{ + }}{V_{ - 4\mu C}}\]
We know that electric potential at a point \[r\] due to charge \[Q\] is calculated as,
Electric potential \[\left( V \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{kQ}}{r}\]
Therefore due the equation can be deduced as.
\[{V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{k\left( { + 4\mu C} \right)}}{r}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{k\left( { + 4\mu C} \right)}}{r}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{k\left( { - 4\mu C} \right)}}{r}\]
The last two terms of the equation will be cancelled out as both are opposite in sign but same in magnitude. Therefore the final potential will be,
\[{V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{k\left( { + 4\mu C} \right)}}{r}{\text{ }}\]
Here \[r\] is same as the distance of centre from vertex which is \[{\text{ }}\dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ cm}}\], \[k{\text{ = 9 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^9}{\text{ N }}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{ }}{{\text{C}}^{ - 2}}\] and \[\mu {\text{ = 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 6}}\]. On substituting the values we get the result as,
\[{V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{ 9 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^9}{\text{ N }}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{ }}{{\text{C}}^{ - 2}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 4 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 6}}{\text{ C}}}}{{\dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ cm}}}}{\text{ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow {V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{ 36}}\sqrt 3 {\text{ }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^3}{\text{ }}}}{{{\text{ 20}}}}{\text{ V }}\]
\[\therefore {V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{9\sqrt 3 }}{5}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^3}{\text{ V }}\]
Hence we get the electric potential at centre of the triangle as \[\dfrac{{9\sqrt 3 }}{5}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^3}{\text{ V }}\].
Note: We cannot ignore the sign of charge present at the vertex of the triangle. Since it is a vector quantity it can be represented as the sum of other vector quantities too. We can also find the centre of a triangle in another way too but the answer would be the same in all cases. The unit of electric potential is volt.
Formula Used:
Electric potential \[ = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{kQ}}{r}\]
Where, \[k = \] Electric constant, \[Q = \] Electric charge and \[r = \] Distance of point from charge $Q$.
Complete step by step answer:
For finding electric potential at the centre of the triangle we need to find the distance of the centre from each vertex of the triangle. Let’s mark this distance as \[x\].Also for finding the position of the centre of a triangle we make perpendicular lines from each vertex. The point where each perpendicular meet is the centre of the triangle. Let’s name this centre of the triangle as C.

Since it is an equilateral triangle, therefore each angle of the triangle will be of \[{60^ \circ }\], therefore \[\angle {\text{CAB = 3}}{0^ \circ }\]. Now in \[\Delta ABC\] we can apply, \[\cos 30{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{10}}{x}\] , because we know that the cosine of angle is the ratio of base and hypotenuse.
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{ }}\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{10}}{x}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{ x = }}\dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ cm}}\]
Now we will find electric potential due to each charge placed at vertex of triangle at the centre of triangle which is at a distance of \[{\text{ }}\dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ cm}}\]. We know that potential is a vector quantity, therefore the electric potential at centre will be the sum of individual potential at centre. Therefore it can calculated as:
\[{V_{net}}{\text{ = }}{V_{ + 4\mu C}}{\text{ + }}{V_{ + 4\mu C}}{\text{ + }}{V_{ - 4\mu C}}\]
We know that electric potential at a point \[r\] due to charge \[Q\] is calculated as,
Electric potential \[\left( V \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{kQ}}{r}\]
Therefore due the equation can be deduced as.
\[{V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{k\left( { + 4\mu C} \right)}}{r}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{k\left( { + 4\mu C} \right)}}{r}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{k\left( { - 4\mu C} \right)}}{r}\]
The last two terms of the equation will be cancelled out as both are opposite in sign but same in magnitude. Therefore the final potential will be,
\[{V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{k\left( { + 4\mu C} \right)}}{r}{\text{ }}\]
Here \[r\] is same as the distance of centre from vertex which is \[{\text{ }}\dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ cm}}\], \[k{\text{ = 9 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^9}{\text{ N }}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{ }}{{\text{C}}^{ - 2}}\] and \[\mu {\text{ = 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 6}}\]. On substituting the values we get the result as,
\[{V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{ 9 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^9}{\text{ N }}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{ }}{{\text{C}}^{ - 2}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 4 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 6}}{\text{ C}}}}{{\dfrac{{20}}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\text{ cm}}}}{\text{ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow {V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{ 36}}\sqrt 3 {\text{ }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^3}{\text{ }}}}{{{\text{ 20}}}}{\text{ V }}\]
\[\therefore {V_{net}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{9\sqrt 3 }}{5}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^3}{\text{ V }}\]
Hence we get the electric potential at centre of the triangle as \[\dfrac{{9\sqrt 3 }}{5}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^3}{\text{ V }}\].
Note: We cannot ignore the sign of charge present at the vertex of the triangle. Since it is a vector quantity it can be represented as the sum of other vector quantities too. We can also find the centre of a triangle in another way too but the answer would be the same in all cases. The unit of electric potential is volt.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




