
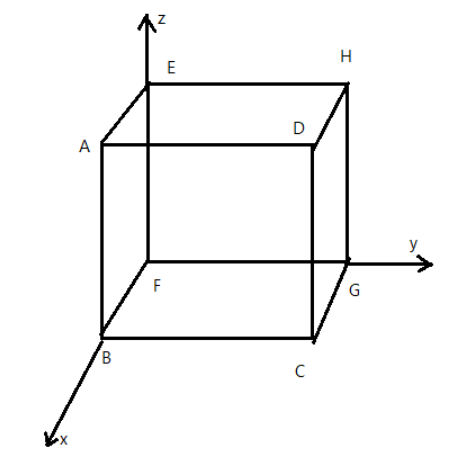
Electric field in a region is given by $E=-4x\hat i+6y\hat j$, find the charge enclosed in the cube side \[1m\] oriented as shown in figure.
\[\begin{align}
& A.2{{\varepsilon }_{0}} \\
& B.zero \\
& C.{{\varepsilon }_{0}} \\
& D.6{{\varepsilon }_{0}} \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Here we have a cube, which is clearly a closed figure. Electric field is the electric force due to a unit positive charge which is at rest would exert on its surrounding. We need to calculate the charge in the cube. But we know that the total charge enclosed in a closed surface is given by Gauss law.
Formula used:
\[{{\Phi }_{_{E}}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\nolimits_E
E\cdot dA \]
Complete answer:
We know that the electric force due to a pair of charges is given by Coulomb's law. An electric field can be produced by a time-varying electric field or an electrical charge. These can be either attracting or repelling in nature.
An electric field $E$ is defined as the electric force $F$ per unit positive charge$q$, which is infinitesimally small and at rest, and is given as
$E=\dfrac{F}{q}$
From Gauss law, we know that the total electric flux through a closed surface is equal to $\dfrac{1}{\epsilon_{0}}$ times the charge enclosed in the surface, and it is given by
$\Phi_{E}=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
Gauss law can also be given as \[{{\Phi }_{_{E}}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\nolimits_E
E\cdot dA \] where \[dA\] is the surface area vector. This form of Gauss law is called the integral form of Gauss law.
Given that $E=-4x\hat i+6y\hat j$ and the charge enclosed in cube side\[1m\], implies $x=y=z=1$
Then $\Phi=6ydy-4xdx=6\times 1\times 1=4\times 1\times 1=6-4=2$
Then from $\Phi_{E}=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$ we get,$2=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
Or,$q=2\epsilon_{0}$
Hence the answer is A.$2\epsilon_{0}$.
Note:
Electric field is in the direction of the force. Usually, the electric field of a point positive charge is radially outwards, whereas the electric field of a point negative charge is radially inwards to the charge. However, the electric field also depends on the symmetry of the charge carrying conductor.
Formula used:
\[{{\Phi }_{_{E}}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\nolimits_E
E\cdot dA \]
Complete answer:
We know that the electric force due to a pair of charges is given by Coulomb's law. An electric field can be produced by a time-varying electric field or an electrical charge. These can be either attracting or repelling in nature.
An electric field $E$ is defined as the electric force $F$ per unit positive charge$q$, which is infinitesimally small and at rest, and is given as
$E=\dfrac{F}{q}$
From Gauss law, we know that the total electric flux through a closed surface is equal to $\dfrac{1}{\epsilon_{0}}$ times the charge enclosed in the surface, and it is given by
$\Phi_{E}=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
Gauss law can also be given as \[{{\Phi }_{_{E}}}=\mathop{{\int\!\!\!\!\!\int}\mkern-21mu \bigcirc}\nolimits_E
E\cdot dA \] where \[dA\] is the surface area vector. This form of Gauss law is called the integral form of Gauss law.
Given that $E=-4x\hat i+6y\hat j$ and the charge enclosed in cube side\[1m\], implies $x=y=z=1$
Then $\Phi=6ydy-4xdx=6\times 1\times 1=4\times 1\times 1=6-4=2$
Then from $\Phi_{E}=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$ we get,$2=\dfrac{q}{\epsilon_{0}}$
Or,$q=2\epsilon_{0}$
Hence the answer is A.$2\epsilon_{0}$.
Note:
Electric field is in the direction of the force. Usually, the electric field of a point positive charge is radially outwards, whereas the electric field of a point negative charge is radially inwards to the charge. However, the electric field also depends on the symmetry of the charge carrying conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




