
What is an electric dipole? Define electric dipole moment.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: As the name suggests dipole is the arrangement that has two (di-) poles. The dipole associated with the electric field is known as an electric dipole. An electric dipole also has a moment which is known as an electric dipole moment. Here we will discuss these two terms that are electric dipole and electric dipole moment.
Formula used:
\[p=qd\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
An electric dipole consists of two equal and opposite point charges, say, -q and +q which are kept d distance apart from each other. The direction of an electric dipole is from –q to +q. The midpoint of the dipole is known as the center of the dipole.
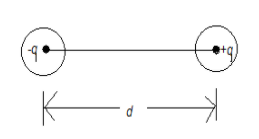
The net charge of the dipole is obviously zero as it has equal and opposite charges but the electric field of the electric dipole is not zero. However, for some points which are very far from the dipole or the distance between the dipole and the point is very large as compared to the distance between the two-point charges of the dipole then the electric field will be canceled out due to equal and opposite point charges.
The electric dipole moment is the product of the charge q with the separation between the two-point charges that are d.
\[p=qd\]
Where p is the electric dipole moment.
The direction of the electric dipole moment is the same as the electric dipole which is from –q to +q. In the case of the point dipole, the separation between the point charges is zero and the charge q approaches infinity such that the electric dipole moment remains finite.
Note: The charges are always equal and opposite in the electric dipole, if there are two opposite charges with different magnitude then it is not considered as an electric dipole. In some cases, the center of both charges lies on the same point in such case the dipole moment is zero.
Formula used:
\[p=qd\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
An electric dipole consists of two equal and opposite point charges, say, -q and +q which are kept d distance apart from each other. The direction of an electric dipole is from –q to +q. The midpoint of the dipole is known as the center of the dipole.

The net charge of the dipole is obviously zero as it has equal and opposite charges but the electric field of the electric dipole is not zero. However, for some points which are very far from the dipole or the distance between the dipole and the point is very large as compared to the distance between the two-point charges of the dipole then the electric field will be canceled out due to equal and opposite point charges.
The electric dipole moment is the product of the charge q with the separation between the two-point charges that are d.
\[p=qd\]
Where p is the electric dipole moment.
The direction of the electric dipole moment is the same as the electric dipole which is from –q to +q. In the case of the point dipole, the separation between the point charges is zero and the charge q approaches infinity such that the electric dipole moment remains finite.
Note: The charges are always equal and opposite in the electric dipole, if there are two opposite charges with different magnitude then it is not considered as an electric dipole. In some cases, the center of both charges lies on the same point in such case the dipole moment is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




