
Ectophloic siphonostele is found in
(a) Adiantum and Cucurbitaceae
(b) Osmunda and Equisetum
(c) Marsilea and Botrychium
(d) Dicksonia and Adiantum
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: The common name for this plant is a royal fern which is derived from its being one of the largest and most imposing European ferns.
Complete answer:
Protostele and Siphonostele are the two principal types of stelar organisation in vascular plants. Stele is a column containing vascular tissues which is surrounded by pericycle and is separated from ground tissue by endodermis. Siphonostele is medullated protostele i.e. having a central non-vascular pith. The leaf gaps are absent.
Siphonostele is of two types:
1. Ectophloic siphonostele: In this type, the central pith is surrounded successively by xylem, phloem, pericycle, and endodermis. It is found in Osmunda and Equisetum.
2. Amphiphloic siphonostele: In this type, there is a central pith, and xylem is surrounded on either side by phloem, pericycle, and endodermis. It is found in Marsilea and Adiantum.
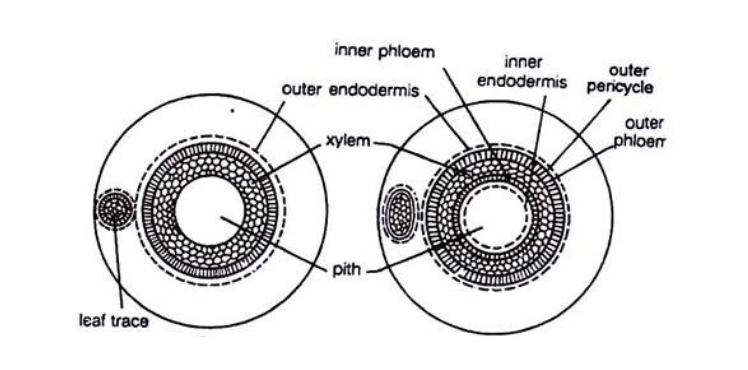
Fig: Left- Ectophloic siphonostele
Right- Amphiphloic siphonostele
Additional Information:
Some modifications of Siphonostele are listed as:
1. Cladosiphonic siphonostele: The siphonostele in which leaf gap is absent is known as cladosiphon siphonostele. Example: Selaginella.
2. Phyllosiphonic siphonostele: The siphonostele in which smaller or larger leaf gaps are there is called phyllosiphonic siphonostele. Example: Filicophyta.
3. Solenostele: The siphonostele which is perforated by scattered leaf traces is known as solenostele.
So, the correct answer is ‘Osmunda and Equisetum’.
Note:
There are two main theories to support the evolution of siphonostele from protostele:
(a) Intraxylary or Intrastelar origin- According to this theory, the siphonostele is evolved by the conversion of the central mass of the xylem into the parenchymatous pith.
(b) Extrastelar Origin: According to this theory, the pith originated as a result of the invasion of parenchymatous cells of the cortex into the stele. This takes place through the leaf gaps and branch gaps. This theory is also famous as invasion theory.
Complete answer:
Protostele and Siphonostele are the two principal types of stelar organisation in vascular plants. Stele is a column containing vascular tissues which is surrounded by pericycle and is separated from ground tissue by endodermis. Siphonostele is medullated protostele i.e. having a central non-vascular pith. The leaf gaps are absent.
Siphonostele is of two types:
1. Ectophloic siphonostele: In this type, the central pith is surrounded successively by xylem, phloem, pericycle, and endodermis. It is found in Osmunda and Equisetum.
2. Amphiphloic siphonostele: In this type, there is a central pith, and xylem is surrounded on either side by phloem, pericycle, and endodermis. It is found in Marsilea and Adiantum.

Fig: Left- Ectophloic siphonostele
Right- Amphiphloic siphonostele
Additional Information:
Some modifications of Siphonostele are listed as:
1. Cladosiphonic siphonostele: The siphonostele in which leaf gap is absent is known as cladosiphon siphonostele. Example: Selaginella.
2. Phyllosiphonic siphonostele: The siphonostele in which smaller or larger leaf gaps are there is called phyllosiphonic siphonostele. Example: Filicophyta.
3. Solenostele: The siphonostele which is perforated by scattered leaf traces is known as solenostele.
So, the correct answer is ‘Osmunda and Equisetum’.
Note:
There are two main theories to support the evolution of siphonostele from protostele:
(a) Intraxylary or Intrastelar origin- According to this theory, the siphonostele is evolved by the conversion of the central mass of the xylem into the parenchymatous pith.
(b) Extrastelar Origin: According to this theory, the pith originated as a result of the invasion of parenchymatous cells of the cortex into the stele. This takes place through the leaf gaps and branch gaps. This theory is also famous as invasion theory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




