
During meiosis, crossing over occurs at
(a) Diplotene
(b) Leptotene
(c) Pachytene
(d) Diakinesis
Answer
534k+ views
Hint: Crossing over occurs at the prophase stage of Meiosis I. It occurs at the longest meiotic stage. Several important events of Meiosis take place during this phase. It begins with the completion of synapsis.
Complete answer:
Crossing over takes place at the pachytene stage of prophase I of Meiosis. Crossing over includes the symmetrical division of chromatids, and the reciprocal exchange and crosswise assembly of segments between non-sister chromatids, often breaking linkage. This results in the recombination of genes. Crossing over generally takes place at the pachytene stage of prophase I of Meiosis I. During the pachytene, stage one chromatid of each homolog overlaps or crosses over a corresponding non-sister chromatid of the other homolog at one or more points. These crossing points are called chiasma. At this point, the non-sister chromatids divide transversely with the help of endonuclease. The broken segments are then mutually interchangeable through them. Each interchanged segment mixes with a corresponding segment of non-sister chromatids with the use of ligases. The complete process which requires the breakage, mutual interchange, and reciprocal reunion of chromosome segments are known as crossing over.
Additional Information:
-Mitotic crossing over involves five major events; synapsis of homologous chromosomes and tetrad formation, crossing over of non-sister chromatids and chiasma formation, symmetrical breakage of non-sister chromatids, reciprocal recombination through the mutual interchange and crosswise assembly of broken segments, dissociation of the homologues through the decriminalization of chiasma.
-Synapsis is known as the close pairing of homologous chromosomes throughout the zygotene stage of the first meiotic division.
-Double-crossing over is the process of crossing over which includes two chiasma and two, three, or four chromatids.
So, the correct answer is 'Pachytene'.
Note:
-Crossing over and the independent assortment of alleles are the primary mechanisms for generating new, non-parental gene combinations and genetic variations.
-Natural selection works upon these recombinant genotypes and genetic variations and therefore improves the fitness, survival value, and evolutionary potentiality of the organisms.
-In eukaryotes, the crossing over could be mitotic or meiotic. Mitotic crossing over takes place in somatic cells and finial cells.
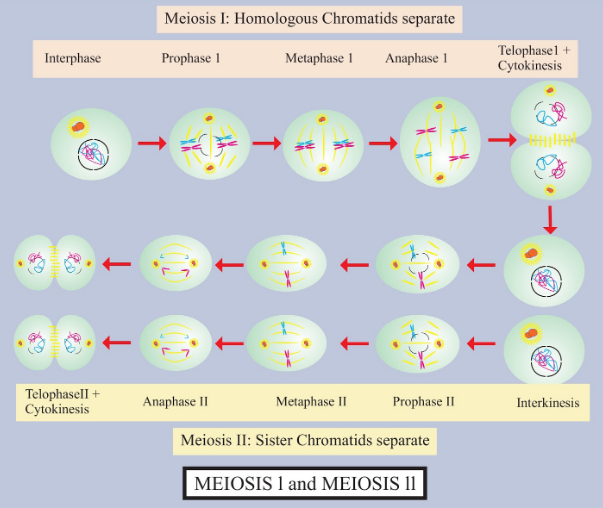
Complete answer:
Crossing over takes place at the pachytene stage of prophase I of Meiosis. Crossing over includes the symmetrical division of chromatids, and the reciprocal exchange and crosswise assembly of segments between non-sister chromatids, often breaking linkage. This results in the recombination of genes. Crossing over generally takes place at the pachytene stage of prophase I of Meiosis I. During the pachytene, stage one chromatid of each homolog overlaps or crosses over a corresponding non-sister chromatid of the other homolog at one or more points. These crossing points are called chiasma. At this point, the non-sister chromatids divide transversely with the help of endonuclease. The broken segments are then mutually interchangeable through them. Each interchanged segment mixes with a corresponding segment of non-sister chromatids with the use of ligases. The complete process which requires the breakage, mutual interchange, and reciprocal reunion of chromosome segments are known as crossing over.
Additional Information:
-Mitotic crossing over involves five major events; synapsis of homologous chromosomes and tetrad formation, crossing over of non-sister chromatids and chiasma formation, symmetrical breakage of non-sister chromatids, reciprocal recombination through the mutual interchange and crosswise assembly of broken segments, dissociation of the homologues through the decriminalization of chiasma.
-Synapsis is known as the close pairing of homologous chromosomes throughout the zygotene stage of the first meiotic division.
-Double-crossing over is the process of crossing over which includes two chiasma and two, three, or four chromatids.
So, the correct answer is 'Pachytene'.
Note:
-Crossing over and the independent assortment of alleles are the primary mechanisms for generating new, non-parental gene combinations and genetic variations.
-Natural selection works upon these recombinant genotypes and genetic variations and therefore improves the fitness, survival value, and evolutionary potentiality of the organisms.
-In eukaryotes, the crossing over could be mitotic or meiotic. Mitotic crossing over takes place in somatic cells and finial cells.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




