
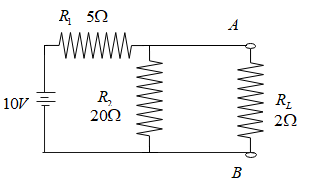
Draw Thevenin’s equivalent circuit and find the voltage across $R_L$, for the given circuit:

Answer
531.3k+ views
Hint: According to Thevenin’s theorem, we can reduce any linear circuit, to an equivalent circuit, such that there exist only one voltage and a series resistance with the given load resistance, this new and simplified circuit is called the Thevenin’s equivalent circuit. Thevenin’s theorem can be used to simplify any complex circuit as well.
Formula used:
$V=IR$
Complete step by step answer:
Clearly the given circuit is a linear circuit, which consists of only resistance and voltages.
To reduce the given circuit into Thevenin’s equivalent circuit, we must first remove the load resistance and calculate the net resistance in the circuit, then the figure looks like this;
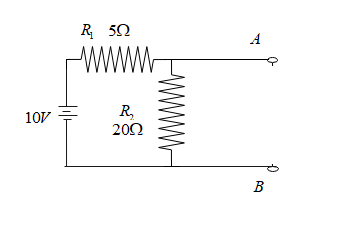
Clearly, $R_1$ and $R_2$are in parallel , then the net resistance $\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{R_1}+\dfrac{1}{R_2}=\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{20}=\dfrac{4+1}{20}=\dfrac{5}{20}=4\Omega$, then the Thevenin’s equivalent circuit, will look as follows:
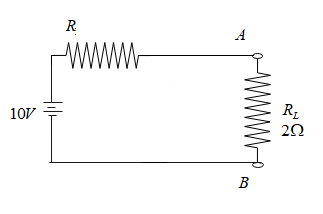
Then the current in the circuit, is given from Ohm’s law as $V=IR_{net}$
Since the load is in series with the resultant of the parallel circuit, we have, $R_{net}=4+2=6\Omega$
Thus, the current in the circuit is given as , $I=\dfrac{V}{R_{net}}=\dfrac{10}{6}=1.66A$
Then the voltage across the load resistance is given as $V_L=IR_L=1.66\times 2=3.33V$
Hence the voltage across the load resistance is $3.33\;V$
Note: A circuit is said to be linear if it contains electrical components like the resistor, inductor and a capacitor, which are passive in nature. However, a circuit is said to be non-linear if it contains active components like semiconductors. Thevenin’s theorem is applicable only to linear circuits.
Here, we have only one source, but if there are multiple sources, then the net of the source is taken into account.
Formula used:
$V=IR$
Complete step by step answer:
Clearly the given circuit is a linear circuit, which consists of only resistance and voltages.
To reduce the given circuit into Thevenin’s equivalent circuit, we must first remove the load resistance and calculate the net resistance in the circuit, then the figure looks like this;

Clearly, $R_1$ and $R_2$are in parallel , then the net resistance $\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1}{R_1}+\dfrac{1}{R_2}=\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{20}=\dfrac{4+1}{20}=\dfrac{5}{20}=4\Omega$, then the Thevenin’s equivalent circuit, will look as follows:

Then the current in the circuit, is given from Ohm’s law as $V=IR_{net}$
Since the load is in series with the resultant of the parallel circuit, we have, $R_{net}=4+2=6\Omega$
Thus, the current in the circuit is given as , $I=\dfrac{V}{R_{net}}=\dfrac{10}{6}=1.66A$
Then the voltage across the load resistance is given as $V_L=IR_L=1.66\times 2=3.33V$
Hence the voltage across the load resistance is $3.33\;V$
Note: A circuit is said to be linear if it contains electrical components like the resistor, inductor and a capacitor, which are passive in nature. However, a circuit is said to be non-linear if it contains active components like semiconductors. Thevenin’s theorem is applicable only to linear circuits.
Here, we have only one source, but if there are multiple sources, then the net of the source is taken into account.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




