
Draw the structure of $Xe{{F}_{4}}$.
Answer
532.8k+ views
Hint: The structure of $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ is governed by the VSEPR theory of electron repulsion. With this idea in mind, try to predict the structure of the given compound.
Step-by-Step Solution:
Before we move onto the structure of $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ , let us first look into the VSEPR theory of electron repulsion.
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Repulsion) theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom.
The number of electron pairs around the central atom can be determined by writing the Lewis structure for the molecule. The geometry of the molecule depends on the number of bonding groups (pairs of electrons) and the number of nonbonding electrons on the central atom.
Now, with the specifics of the VSEPR theory done and accounted for, let us now move on to the specific structure of $Xe{{F}_{4}}$.
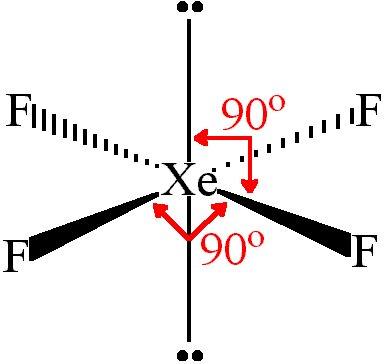
VSEPR theory predicts that $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ is square planar. There are six electron pairs around the central atom (Xe), four of which are bonding, and two are lone pairs. Thus, we have octahedral electron pair geometry, and square planar molecular geometry.
It’s possible that someone might tell you that xenon exhibits \[sp{}^\text{3}d{}^\text{2}\] hybridization. Don’t believe that. It’s been pretty well established that for the representative elements there is no d-orbital participation in the bonding in hypervalent molecules.
Note: While a traditional compound unlike $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ such as xenon hexafluoride ($Xe{{F}_{6}}$) without the presence of lone pairs in its structure would exhibit octahedral geometry with different bond angles, the presence of lone pairs increases electron repulsions leading to a square planar structure with 900 bond angles.
Step-by-Step Solution:
Before we move onto the structure of $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ , let us first look into the VSEPR theory of electron repulsion.
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Repulsion) theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom.
The number of electron pairs around the central atom can be determined by writing the Lewis structure for the molecule. The geometry of the molecule depends on the number of bonding groups (pairs of electrons) and the number of nonbonding electrons on the central atom.
Now, with the specifics of the VSEPR theory done and accounted for, let us now move on to the specific structure of $Xe{{F}_{4}}$.
VSEPR theory predicts that $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ is square planar. There are six electron pairs around the central atom (Xe), four of which are bonding, and two are lone pairs. Thus, we have octahedral electron pair geometry, and square planar molecular geometry.

It’s possible that someone might tell you that xenon exhibits \[sp{}^\text{3}d{}^\text{2}\] hybridization. Don’t believe that. It’s been pretty well established that for the representative elements there is no d-orbital participation in the bonding in hypervalent molecules.
Note: While a traditional compound unlike $Xe{{F}_{4}}$ such as xenon hexafluoride ($Xe{{F}_{6}}$) without the presence of lone pairs in its structure would exhibit octahedral geometry with different bond angles, the presence of lone pairs increases electron repulsions leading to a square planar structure with 900 bond angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




