
Draw the structure of diborane.
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: The two atoms of boron left with that of each unpaired electron orbital and empty orbital forms the two bridging (B–H–B) bonds with that of the two 1s hydrogen atoms, is also called the banana bond. Keep this in mind when trying to figure out the resultant structure of diborane.
Step-by-Step Solution:
Let us first analyse the chemical properties of Diborane before moving onto its structural analysis.
Diborane is the chemical compound consisting of boron and hydrogen with the formula \[{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}\]. It is a colourless, pyrophoric gas with a repulsively sweet odour. Synonyms include boro-ethane, boron hydride, and di-boron hexahydride. Diborane is a key boron compound with a variety of applications. It has attracted wide attention for its electronic structure. Its derivatives are useful reagents.
Let us now move onto the structural analysis of Diborane.
The model determined by molecular orbital theory describes the bonds between boron and the terminal hydrogen atoms as conventional 2-center, 2-electron covalent bonds. The bonding between the boron atoms and the bridging hydrogen atoms is, however, different from that in molecules such as hydrocarbons.
Each boron uses two electrons in bonding to the terminal hydrogen atoms, and has one valence electron remaining for additional bonding. The bridging hydrogen atoms provide one electron each. The \[{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}\] ring is held together by four electrons which form two 3-center 2-electron bonds. This type of bond is sometimes called a 'banana bond'.
Therefore mentioned structure is drawn as follows:
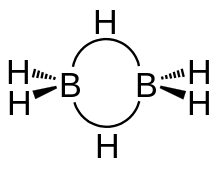
Note: The boron atom is known to be \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridized and has four hybrid orbitals. From these four hybrid orbitals, three of the orbitals have one electron each, and of which one is an empty orbital.
Step-by-Step Solution:
Let us first analyse the chemical properties of Diborane before moving onto its structural analysis.
Diborane is the chemical compound consisting of boron and hydrogen with the formula \[{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}\]. It is a colourless, pyrophoric gas with a repulsively sweet odour. Synonyms include boro-ethane, boron hydride, and di-boron hexahydride. Diborane is a key boron compound with a variety of applications. It has attracted wide attention for its electronic structure. Its derivatives are useful reagents.
Let us now move onto the structural analysis of Diborane.
The model determined by molecular orbital theory describes the bonds between boron and the terminal hydrogen atoms as conventional 2-center, 2-electron covalent bonds. The bonding between the boron atoms and the bridging hydrogen atoms is, however, different from that in molecules such as hydrocarbons.
Each boron uses two electrons in bonding to the terminal hydrogen atoms, and has one valence electron remaining for additional bonding. The bridging hydrogen atoms provide one electron each. The \[{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}\] ring is held together by four electrons which form two 3-center 2-electron bonds. This type of bond is sometimes called a 'banana bond'.
Therefore mentioned structure is drawn as follows:

Note: The boron atom is known to be \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridized and has four hybrid orbitals. From these four hybrid orbitals, three of the orbitals have one electron each, and of which one is an empty orbital.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




