
Draw the structure of a major monohalo product in each of the following reactions.

Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: If one or more of the hydrogen atoms are being replaced by an equivalent number of the halogens in a hydrocarbon, the final compounds attained are known as halogen derivatives of hydrocarbons.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Depending on the number of halogen atoms in the halogen derivatives of hydrocarbons are known as monohalogen or polyhalogen derivatives of hydrocarbons. Let us draw the structure of a major monohalo product by completing each of the given reactions one by one.
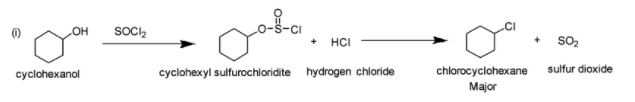
(i) \[SOC{l_2}\]i.e. thionyl chloride is generally used to prepare alkyl chlorides from alcohols. In the given reaction, cyclohexanol is made to react with thionyl chloride. The hydroxyl oxygen (of cyclohexanol) attacks the electrophilic Sulfur (of thionyl chloride) which leads to the formation of chlorosulfite ester (cyclohexyl sufurochloridite) and hydrogen chloride. The chlorosulfite ester then rearranges with the breaking of C-O and S-Cl bonds and leads to the formation of chlorocyclohexane and sulphur dioxide. The reaction is depicted below:
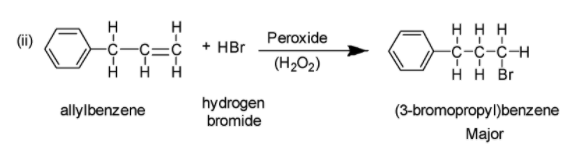
(ii) Addition reaction of allyl benzene in the presence of peroxide generally yields (3-bromopropyl)benzene in accordance with anti-Markovnikov rule of addition. According to anti-Markovnikov rule, the hydrogen atom of HX in an addition reaction of generic electrophile HX to either an alkene or alkyne, becomes bonded to carbon atom having the least number of hydrogen atoms in the starting alkyne or alkene. The reaction is depicted below:
Note: The major difference between Markovnikov and anti-Markovnikov rule is that Markinov rule states that in an addition reaction, hydrogen atoms are linked to the carbon atom having more hydrogen substituents while anti-Markovnikov rule states that in an addition reaction, hydrogen atoms are linked to the carbon atom having the least hydrogen substituents.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Depending on the number of halogen atoms in the halogen derivatives of hydrocarbons are known as monohalogen or polyhalogen derivatives of hydrocarbons. Let us draw the structure of a major monohalo product by completing each of the given reactions one by one.
(i) \[SOC{l_2}\]i.e. thionyl chloride is generally used to prepare alkyl chlorides from alcohols. In the given reaction, cyclohexanol is made to react with thionyl chloride. The hydroxyl oxygen (of cyclohexanol) attacks the electrophilic Sulfur (of thionyl chloride) which leads to the formation of chlorosulfite ester (cyclohexyl sufurochloridite) and hydrogen chloride. The chlorosulfite ester then rearranges with the breaking of C-O and S-Cl bonds and leads to the formation of chlorocyclohexane and sulphur dioxide. The reaction is depicted below:

(ii) Addition reaction of allyl benzene in the presence of peroxide generally yields (3-bromopropyl)benzene in accordance with anti-Markovnikov rule of addition. According to anti-Markovnikov rule, the hydrogen atom of HX in an addition reaction of generic electrophile HX to either an alkene or alkyne, becomes bonded to carbon atom having the least number of hydrogen atoms in the starting alkyne or alkene. The reaction is depicted below:

Note: The major difference between Markovnikov and anti-Markovnikov rule is that Markinov rule states that in an addition reaction, hydrogen atoms are linked to the carbon atom having more hydrogen substituents while anti-Markovnikov rule states that in an addition reaction, hydrogen atoms are linked to the carbon atom having the least hydrogen substituents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




