
Draw the structure and name the product formed if the following alcohols are oxidized. Assume that an excess of oxidizing agent is used:
(i) $C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$
(ii) $2 -$butenol
(iii) $2 -$methyl - propanol
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Primary alcohols get oxidised to carboxylic acid in the presence of excess oxidising agents. Enols only get oxidised to the corresponding enals (aldehyde) since the double bond prevents further oxidation. Only the functional groups are affected during oxidation. Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen/removal of hydrogen from a molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
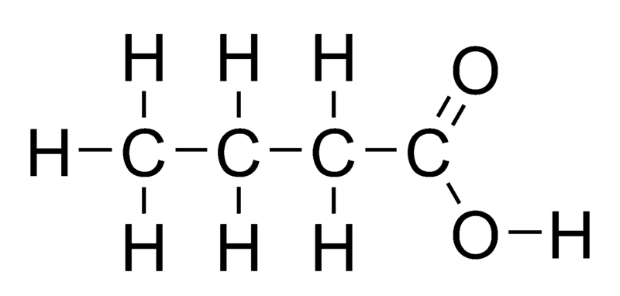
The first compound is butanol, which is a primary alcohol. As we know, primary alcohols get oxidised to carboxylic acids in the presence of excess oxidising agents. Thus, the product formed here is butanoic acid.
$C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH\xrightarrow{{[O]}}C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$
Its structure is given below:
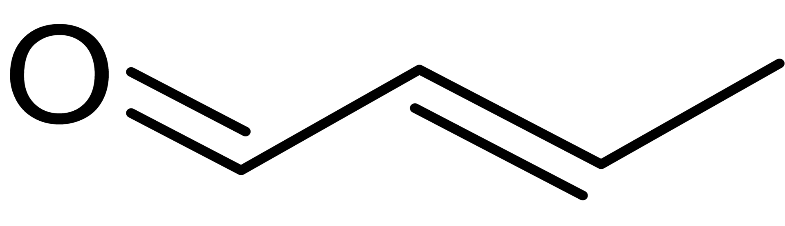
(ii) The second compound is an enol, that is, a compound with a double bond and an alcohol group. Enols can only be oxidised by mild oxidising agents and they form the corresponding enals as the product. Hence, in this in case, we get $2-$butenal as the product:
$C{H_3} - CH = CH - C{H_2}OH\xrightarrow{{[O]}}C{H_3} - CH = CH - CHO$
Its structure is given below:
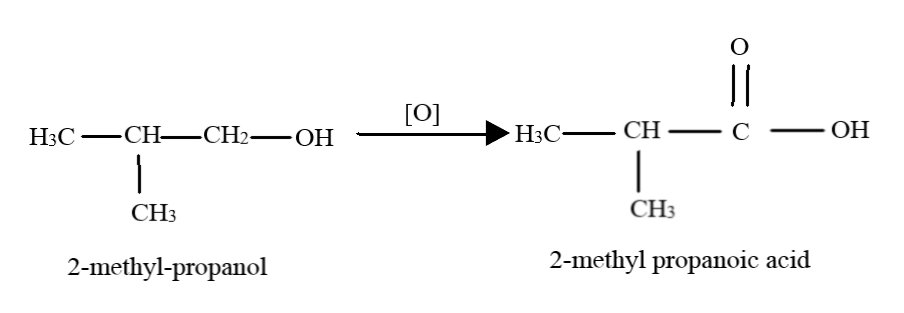
(iii) The third compound is again a primary alcohol, and thus, it gets oxidised to a carboxylic acid in presence of excess reagent. The methyl group is left unaffected. Thus, the product here is $2 - $ methyl-propanoic acid.
Note: When primary alcohols are oxidised normally, the product obtained are aldehydes. Only in the presence of strong oxidising agents or in the presence of excess oxidising agents do the aldehydes get oxidised further to yield the carboxylic acids. Note that secondary alcohols get oxidised to ketones first, which may undergo further oxidation to give a mixture of carboxylic acids. Tertiary alcohols, however, cannot be oxidised at normal conditions.
Complete step by step answer:
The first compound is butanol, which is a primary alcohol. As we know, primary alcohols get oxidised to carboxylic acids in the presence of excess oxidising agents. Thus, the product formed here is butanoic acid.
$C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH\xrightarrow{{[O]}}C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}COOH$
Its structure is given below:

(ii) The second compound is an enol, that is, a compound with a double bond and an alcohol group. Enols can only be oxidised by mild oxidising agents and they form the corresponding enals as the product. Hence, in this in case, we get $2-$butenal as the product:
$C{H_3} - CH = CH - C{H_2}OH\xrightarrow{{[O]}}C{H_3} - CH = CH - CHO$
Its structure is given below:

(iii) The third compound is again a primary alcohol, and thus, it gets oxidised to a carboxylic acid in presence of excess reagent. The methyl group is left unaffected. Thus, the product here is $2 - $ methyl-propanoic acid.

Note: When primary alcohols are oxidised normally, the product obtained are aldehydes. Only in the presence of strong oxidising agents or in the presence of excess oxidising agents do the aldehydes get oxidised further to yield the carboxylic acids. Note that secondary alcohols get oxidised to ketones first, which may undergo further oxidation to give a mixture of carboxylic acids. Tertiary alcohols, however, cannot be oxidised at normal conditions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




